Banswara is a city located in the Banswara District in the south of the state of Rajasthan in India. The exact geographical location of Banswara , Rajasthan is 23.55° North and 74.45° East. It has a mean elevation of 302 meters (990 feet). Maharawal Jagmal Singh established the princely state of Banswara , Rajasthan. Banswara , Rajasthan derives its name from the abundance of "bans" or bamboo forests. The Mahi River, which flows through Banswara , Rajasthan, is home to many islands. For this reason, the city of Banswara is also known as `City of Hundred Islands`. Banswara District covers an area of 5,037 square km, which is about 1.47% of the entire Rajasthan state. The district headquarters are located in the city of Banswara. As boundaries it has the Udaipur District on the north, the Chittorgarh District on the northeast, the state of Madhya Pradesh on the east and southeast, the state of Gujarat on the southwest, and the Dungarpur District on the west. The District of Banswara is situated in the Mahi River basin. The Mahi originates in the Vindhya Range of Madhya Pradesh, comes into the district from the southeast and flows north towards the northern end of the district, where it turns southwest and forms the boundary between Banswara and Dungarpur districts before entering Gujarat and merging with the Gulf of Cambay. Banswara district is included under the Vagad region of southern Rajasthan, which incorporates Banswara and Dungarpur districts. Tribals, mainly those of the Bhil community, principally inhabit the region. The flora and fauna of Banswara District is very rich. The forests contains primarily teak. The wildlife consists of a great diversity of wild animals like leopard, chinkara and the like. Birds commonly found in the region are fowl, black drongo, partridge, grey shrike, bulbul, parrot, green bee-eater and many others.
Geography of Banswara
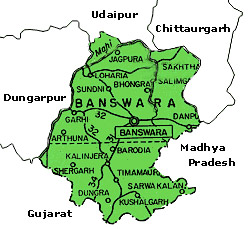 The district of Banswara lies in the southern most part of Rajasthan. It is surrounded by Udaipur and Chittaurgarh in the North, Dungarpur in the west, Ratlam and Jhabua districts of Madhya Pradesh in the east and south. The area of the district is 5,037 km², which constitutes 1.47% of Rajasthan state. The district lies in theMahi River basin. Banswara is part of Vagad region of southern Rajasthan, which includes Banswara and Dungarpur districts. The district comprises of territories of former Banswara State and the Chieftainship of Kushalgarh. The central and western portion of the district are fertile plains, the scattered ranges of the Aravallis form the eastern region. The ancient town is surrounded by a stonewall, which are now in ruins. Banswara state is about 45 m. in length from N. to S., and 33 m. in breadth from E. to W., and has an area of 1946 sq. m. Mahi is the only river of the state and there is scarcity in the state during dry season.
As Banswara is located in the Southern part of Rajasthan, the state experiences a milder climate than that of North and West Rajasthan. During the summers, the temperature in and around Banswara remains quite high like other parts of Rajasthan. In winters the temperature of Banswara goes down due to the Desert landscape of Rajasthan. The highest temperature during winter months remains around 20° C. Maximum temperature is 33 degrees Celsius to 46 degrees Celsius. Minimum temperature is 10 degrees Celsius to 20 degrees Celsius. Normal annual rainfall of the state is 92.24 cms.
The district of Banswara lies in the southern most part of Rajasthan. It is surrounded by Udaipur and Chittaurgarh in the North, Dungarpur in the west, Ratlam and Jhabua districts of Madhya Pradesh in the east and south. The area of the district is 5,037 km², which constitutes 1.47% of Rajasthan state. The district lies in theMahi River basin. Banswara is part of Vagad region of southern Rajasthan, which includes Banswara and Dungarpur districts. The district comprises of territories of former Banswara State and the Chieftainship of Kushalgarh. The central and western portion of the district are fertile plains, the scattered ranges of the Aravallis form the eastern region. The ancient town is surrounded by a stonewall, which are now in ruins. Banswara state is about 45 m. in length from N. to S., and 33 m. in breadth from E. to W., and has an area of 1946 sq. m. Mahi is the only river of the state and there is scarcity in the state during dry season.
As Banswara is located in the Southern part of Rajasthan, the state experiences a milder climate than that of North and West Rajasthan. During the summers, the temperature in and around Banswara remains quite high like other parts of Rajasthan. In winters the temperature of Banswara goes down due to the Desert landscape of Rajasthan. The highest temperature during winter months remains around 20° C. Maximum temperature is 33 degrees Celsius to 46 degrees Celsius. Minimum temperature is 10 degrees Celsius to 20 degrees Celsius. Normal annual rainfall of the state is 92.24 cms.
Banswara , Rajasthan has been ruled in progression by many kings and rulers. It was established in the 16th century by a line of the Acharaya Vansh Kings who were followers of the Kabir Panth, a religious group that advocates the unanimity of all religions and the omnipresence of the almighty. The names of most of the early kings have been forgotten with the exception of Mahant Shri Amardasji Saheb, who ruled around four hundred years ago and was known far and wide for his generous heart and expertise in different religions. From the time of Mahant Shri Amardasji Saheb, the throne has been chronologically handed down to sons or heirs in order from Mahant Shri Amardasji Saheb to Mahant Shri Tulsidasji Saheb, Mahant Shri Kalidasji Saheb, Mahant Shri Devidasji Saheb, Mahant Shri Pavandasji Saheb and finally to Mahant Shri Karan Pratap Singh Saheb. Although The prince is presently ruling together with his father, The throne has already been handed over ceremonially to the young prince who, along with his father dwells in the United States of America.
Divisions of Banswara , Rajasthan
The district is divided into two sub-divisions as Banswara and Kushalgarh. The Banswara sub-division consists of Ghatol, Pipal Khunt, Garhi and Talwara Panchayat Samitis whereas the Kushalgarh sub-division consists of Bagidora, Anandpuri, Sajjangarh and Kushalgarh Panchayat Samitis.
Demography of Banswara , Rajasthan
According to the 2001 India census, the population of Banswara is 85,638. Males and females respectively make up 52% of the population and females constitute 48%. Banswara has a mean literacy rate of 74%, higher than the nationwide mean of 59.5%. 56% of the males and 44% of the females are literate. 13% of the population is children below six years of age.
Flora and fauna of Banswara , Rajasthan
 Banswara District has rich flora and fauna. Teaks are found in abundance in the forests of Banswara. The fauna includes a large variety of wild animals like leopard, chinkara etc. There are squirrels, lizards, snakes, chinkara, Ronj and four horned antelope. Panthers can be seen rarely.
Banswara District has rich flora and fauna. Teaks are found in abundance in the forests of Banswara. The fauna includes a large variety of wild animals like leopard, chinkara etc. There are squirrels, lizards, snakes, chinkara, Ronj and four horned antelope. Panthers can be seen rarely.
Common birds found here are fowl, partridge, black drongo, grey shrike, green bee-eater, bulbul, parrot, jungle crow, wood pecker and common myna.
Economy of Banswara , Rajasthan
The industries of Banswara are agro-based industries (oil mills), industries for dress materials, blended yarn, shirting and suiting, synthetic yarn and texturised grey cloth yarn, marble slabs and tiles and Portland cement. There are eight large and medium scale units and 5312 small-scale units. The world-class manufacturer of Yarn & Fabric is the Banswara Syntex Limited (BSL). The company has three marketing divisions for yarn, fabrics and ready made garments.
Banswara is an agricultural market center. The crops grown in Banswara are wheat, maize, rice, soyabeans, gram, sugarcane, black gram, barley, jowar, groundnuts, fenugreek seeds, bajra and green gram.
The minerals found here are limestone, masonary stone, marble blocks, limestone and sand.
Transportation of Banswara , Rajasthan
Banswara is well connected to other places by means of road and air. The district headquarters has direct road connection with Ratlam, Dungarpur, Dohad and Jaipur. The total road length in the district is 1,747 kms. The nearest railway station is at Dungarpur (102 kms.), which is on meter gauge. The nearest airport of Banswara is at Udaipur.
Education of Banswara , Rajasthan
There are 4 colleges, 128 higher secondary and secondary schools, 1,995 primary and middle schools and 2 ITI centers at Banswara.
Places of attraction in Banswara , Rajasthan
 The places to visit in Banswara are Dialab Lake, Anand Sagar Lake or Bai Talab, Madareshwar, Raghunath Mandir, Abdulla Pir, Phati Khan-Talwara, Sai Mandir
and Shri Satya Kabir Mandir (created by the king Mahant Shri Pavandassji Saheb). There are many places for excursions such as Kagdi Pikup Wear, Talwara, Tripura Sundari, Mahi dam, Chinch, Arthuna, Parahera and Sitamata Wildlife Sanctuary.
The places to visit in Banswara are Dialab Lake, Anand Sagar Lake or Bai Talab, Madareshwar, Raghunath Mandir, Abdulla Pir, Phati Khan-Talwara, Sai Mandir
and Shri Satya Kabir Mandir (created by the king Mahant Shri Pavandassji Saheb). There are many places for excursions such as Kagdi Pikup Wear, Talwara, Tripura Sundari, Mahi dam, Chinch, Arthuna, Parahera and Sitamata Wildlife Sanctuary.
Fairs and festivals of Banswara
•Holi
•Emi Egyaras
•Ghotia Amba Fair
•Mangarh Fair



















