 Anaemia is the most common disorder of the blood which usually means "without blood". This is defined as a qualitative or quantitative deficiency of haemoglobin. Haemoglobin is a molecule inside Red Blood Cells (RBC). As haemoglobin carries oxygen from the lungs to the tissues, Anaemia leads to hypoxia i.e. lack of oxygen in organs. Since all human cells depend on oxygen for survival, varying degrees of anaemia can have a wide range of clinical consequences.
Anaemia is the most common disorder of the blood which usually means "without blood". This is defined as a qualitative or quantitative deficiency of haemoglobin. Haemoglobin is a molecule inside Red Blood Cells (RBC). As haemoglobin carries oxygen from the lungs to the tissues, Anaemia leads to hypoxia i.e. lack of oxygen in organs. Since all human cells depend on oxygen for survival, varying degrees of anaemia can have a wide range of clinical consequences.
Types of Anaemia
The three main classes of anaemia include excessive blood loss, excessive blood cell destruction or deficient red blood cell production or ineffective haematopoiesis. There are several kinds of anaemia, produced by a variety of underlying causes. Anaemia can be classified in a variety of ways, based on the morphology of RBCs, underlying etiologic mechanisms, and discernible clinical spectra, to mention a few.
Causes of Anaemia
Anaemia may be caused by loss of blood through excessive menstruation, injury, childbirth, bleeding from the gastro-intestinal tract. Certain diseases like Purpura and haemophilia, which are characterized by bleeding, can also be the cause. Defective blood formation because of infections, toxins, and drugs and also inadequate intake of iron and defective absorption of substances in the diet, which enrich the blood, are the causes. Some anaemia is caused due to a combination of more than one of the causes enumerated above.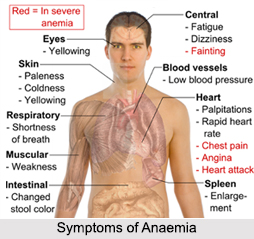
Symptoms of Anaemia
The most striking symptom of anaemia is the pallor of the skin; hence the Ayurvedic name of the disease is "Pandu Roga". The best guide, however, is the colour of the internal lining of the eyelid. There is weakness and giddiness, the breathing is shallow, the pulse rapid, and the blood pressure is often becomes low. In severe cases, the tongue is often sore and the nails of the fingers brittle and concave instead of being convex. If the disease is ignored, it may turn into "Pernicious Anaemia", which is more difficult to cure. In some severe cases, the patient may have to be given a blood transfusion to make up the loss of blood. Usually blood transfusion happens in traumas like severe haemorrhage due to injury or bursting of an ulcer in the abdominal region.
Treatment of Anaemia
There is a range of treatments for anaemia, all ultimately aimed at increasing the red blood cell count which in turn increases the amount of oxygen the blood carries. If the anaemia is caused by nutritional deficiencies, a change to an iron-rich diet can help alleviate the symptoms. The exact cause of the malady should be ascertained before starting the treatment. Fruit juice, milk, meat soup, green vegetables, and light foods free from fats and sour substances are recommended for a patient suffering from anaemia. Sweet mango is like nectar for such a patient.




