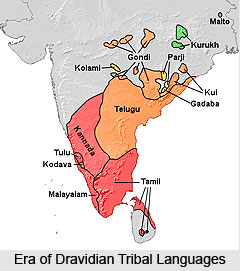
 The group of Dravidian tribal languages are spoken by near about 158 million people. They account for a total of 24 per cent of the total population of the country. In the Dravidian language group there are basically four prominent literary languages and these are Telugu, Malayalam, Kannada and Tamil. Along with these major languages, two more languages that are Coorgi or Kodagu and Tulu are not counted as the Dravidian tribal languages. It is because of the fact that these languages have been merged into Kannada language.
The group of Dravidian tribal languages are spoken by near about 158 million people. They account for a total of 24 per cent of the total population of the country. In the Dravidian language group there are basically four prominent literary languages and these are Telugu, Malayalam, Kannada and Tamil. Along with these major languages, two more languages that are Coorgi or Kodagu and Tulu are not counted as the Dravidian tribal languages. It is because of the fact that these languages have been merged into Kannada language.
In the Dravidian tribal languages family, 147 mother tongues have been included. The most important among them are Kolami, Kui, Konda, Koya, Gondi, Oraon/Kurukh, Parji and more. Little information is available regarding the Dravidian tribal languages. Kadar is one of the popular Dravidian languages and it is quite similar to the Malayalam language. This Dravidian language is mainly spoken by some scheduled tribe communities in areas of Kerala like Palghat, Trichur and Ernakulam and also in some parts of Andhra Pradesh and also in areas of Coimbatore district in Tamil Nadu.
Kaikadi is another major Dravidian tribal language that is spoken by the Kaikadi tribes in several parts of Karnataka and Maharashtra. Kamar, another tribal language belonging to the Dravidian family is spoken by the tribal communities of areas of Rewa district of the state of Madhya Pradesh and in Raipur district of the state of Chattisgarh. Another Dravidian tribal language is Kanikkaran that is spoken in Ernakulam, Thiruvananthapuram and Kozikhode districts of Kerala and Tirunelveli district of the state of Tamil Nadu. Khirwar Dravidian tribal language is mainly spoken by the Khirwar tribal group of Sarguja district of the state of Madhya Pradesh. Dravidian tribal language family also includes Kolami language, which is spoken by the tribes of Adilabad district of the state of Andhra Pradesh. It is also spoken by the tribes of Nanded district and Chandrapur district of Maharashtra. Its main dialects are Asifabad, Naiki and Utnur.
Konda-Dora is a Dravidian language and it is spoken in several areas of Orissa and Andhra Pradesh. Koraga is spoken in parts of Kerala. Kota is another hugely spoken Dravidian language. It is mainly spoken in parts of Tamil Nadu. Koya is spoken in several parts of Madhya Pradesh, Orissa, Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh. Its main dialects are Podia, Malakanagiri Koya, Chintoor Koya, etc.
Thus, it can be said that the Dravidian tribal languages are mainly spoken in parts of Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Maharashtra and Orissa.




