 Natural Vegetation in India refers to a plant community which has grown naturally by following the climatic variables. They have been left undisturbed by humans for a long time. India is bestowed with a wide range of flora and fauna. Due to a diverse geographical and climatic condition, an extensive range of natural vegetation grows in India. Natural Vegetation in India is influenced by a few factors like topography, soil, amount of rainfall and temperature.
Natural Vegetation in India refers to a plant community which has grown naturally by following the climatic variables. They have been left undisturbed by humans for a long time. India is bestowed with a wide range of flora and fauna. Due to a diverse geographical and climatic condition, an extensive range of natural vegetation grows in India. Natural Vegetation in India is influenced by a few factors like topography, soil, amount of rainfall and temperature.
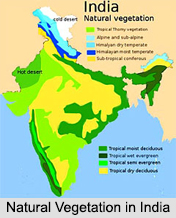
Types of Natural Vegetation in India
Natural Vegetation in India can be classified in different ways, according to their position, atmosphere, weather condition, etc. Some of the common characteristics of various types of natural vegetation in India include the Tropical Rain Forest, the Tropical Deciduous Forests, the Temperate Forests and Grasslands, the Alpine and Tundra Vegetation, etc.
Tropical Rain Forests: The tropical rain forests play an important role in natural vegetation in India. These types of forests include the tropical evergreen forests and tropical semi-evergreen forests and they are mostly found in places where there is plenty of rainfall and sunshine throughout the year. Such regions are limited within rainy slopes of the Western Ghats, plains of West Bengal and Odisha and North-eastern India.
 Tropical Deciduous Forests: They are called as deciduous as they cast leaves for about 6 to 8 weeks in summer. They are also called the monsoon forests with all their grandeur and beauty. This is so because they form a natural cover approximately all over India, especially within regions having 200 and 75 cm of annual rainfall. Most of the tropical deciduous forests are found in the state of Kerala in India. Apart from Kerala, these forests can be found in the eastern slopes of Western Ghats and also in the north-eastern parts of the peninsular plateau and in the valleys of the Himalaya mountains.
Tropical Deciduous Forests: They are called as deciduous as they cast leaves for about 6 to 8 weeks in summer. They are also called the monsoon forests with all their grandeur and beauty. This is so because they form a natural cover approximately all over India, especially within regions having 200 and 75 cm of annual rainfall. Most of the tropical deciduous forests are found in the state of Kerala in India. Apart from Kerala, these forests can be found in the eastern slopes of Western Ghats and also in the north-eastern parts of the peninsular plateau and in the valleys of the Himalaya mountains.
Semi-Deserts and Deserts Vegetations: The Semi-deserts and Deserts vegetations offer another kind of natural vegetation in India. These forests are mainly found in dry places where the annual rainfall is less than 70 cm. They are stretched over the north-western part of India, from Saurashtra to Punjab plains in the north. In the east, the thorn forests and shrubs extend towards northern Madhya Pradesh (primarily Malwa Plateau) and south-west Uttar Pradesh, covering Bundelkhand plateau.
 Tidal or Mangrove Forests: The tidal forests provide another variety of Natural Vegetation in India. They can be found along the coasts and rivers and they are enshrouded by mangrove trees that can live in both fresh and salt water. Sundari is a renowned mangrove tree, mainly found in the tidal forests and it is after this tree that the name Sundarban has been entitled to the forested parts of the Ganga-Brahmaputra delta.
Tidal or Mangrove Forests: The tidal forests provide another variety of Natural Vegetation in India. They can be found along the coasts and rivers and they are enshrouded by mangrove trees that can live in both fresh and salt water. Sundari is a renowned mangrove tree, mainly found in the tidal forests and it is after this tree that the name Sundarban has been entitled to the forested parts of the Ganga-Brahmaputra delta.
Mountain Forests: Natural vegetation in India can be found in the Mountain forests as well. Various types of plants are found in the Himalayas in relation to the varying altitudes. They are mainly found in the southern slopes of the Himalayas. The temperate grasslands are also commonly seen at higher altitudes in these regions.
 Alpine and Tundra Vegetation: Vegetation growing at altitudes above 3.6 km MSL is usually known as Alpine Vegetation. The Alpine Grasslands are mainly found at higher altitudes in this region.
Alpine and Tundra Vegetation: Vegetation growing at altitudes above 3.6 km MSL is usually known as Alpine Vegetation. The Alpine Grasslands are mainly found at higher altitudes in this region.
All these varieties of forests and areas significantly contribute to the Natural Vegetation in India. But there are several problems like deforestation, over-grazing, Jhum cultivations, which needs to be addressed in order to protect and conserve the Natural Vegetation in India. The Government of India is taking several steps to spread awareness about the need for conservation and has educated the general civilians about the several measures that need to be adopted in order to protect the Natural Vegetation in India.











