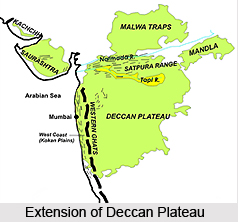
 Deccan Plateau is a home to a large number and variety of habitats and it covers most of the marts of southern and central India. The western boundary of the Deccan Plateau is formed by the Western Ghats, and it eastern boundary is formed by the Eastern Ghats. Both rise from their respective closely-located coastal plains and roughly reach the tip of southern India. Both the ranges form the southward-aiming vertex of a triangle, which comprehends the plateau with the approximately west-southwest to east-north-east running Vindhya Mountain Range and Satpura Mountain Range shaping the third northern boundary of the Deccan Plateau. The northern ranges separate the Deccan Plateau from the densely populated riverine plains of the northern parts of India. Most of the areas of the Indian state of Karnataka and Maharashtra and some parts of the state of Andhra Pradesh form the Deccan plateau.
Deccan Plateau is a home to a large number and variety of habitats and it covers most of the marts of southern and central India. The western boundary of the Deccan Plateau is formed by the Western Ghats, and it eastern boundary is formed by the Eastern Ghats. Both rise from their respective closely-located coastal plains and roughly reach the tip of southern India. Both the ranges form the southward-aiming vertex of a triangle, which comprehends the plateau with the approximately west-southwest to east-north-east running Vindhya Mountain Range and Satpura Mountain Range shaping the third northern boundary of the Deccan Plateau. The northern ranges separate the Deccan Plateau from the densely populated riverine plains of the northern parts of India. Most of the areas of the Indian state of Karnataka and Maharashtra and some parts of the state of Andhra Pradesh form the Deccan plateau.
The Deccan Plateau is situated to the south of the Indo-Gangetic plain. The forests of this plateau are comparatively dry but serve to hold the rain in order to form streams which ultimately feed into rivers flowing into the basins and then into the Bay of Bengal.
The Godavari River along with its tributaries, which include the Indravati River, drains a majority of the northern areas of the plateau, ascending in the Western Ghats and flowing towards east to the Bay of Bengal. The Krishna River, the Tungabhadra River and its tributaries which include the Bhima River, which also runs from the western direction to the east, drain the plateau`s central parts. The Kaveri River drains the southernmost portion of the Deccan plateau, which rises in Karnataka`s Western Ghats and bends to the direction of south in order to move through the Nilgiri hills at Hogenakal Falls into the state of Tamil Nadu, thus making the Sivasamudram Falls at the island town of Shivanasamudra, which is also regarded as India`s second biggest waterfall and the World`s sixteenth largest, before flowing through the Stanley Reservoir and the Mettur Dam which formed the reservoir and lastly emptying its water into the Bay of Bengal. River Tapi and Narmada River are the two rivers which do not flow into the Bay of Bengal. They start their journey in the Eastern Ghats and empty into the Arabian Sea.
Deccan Plateau`s immense volcanic basalt beds were established in the massive Deccan Traps eruption, which took place towards the end of the Cretaceous period, roughly between 67 and 65 million years ago. This volcanic hotspot which formed the Deccan traps is assumed to be positioned under the present day Reunion Island in the Indian Ocean. This plateau is also very rich in minerals. Some of the primary mineral ores available in this region are iron ore and mica in the Chhota Nagpur region, and gold, diamonds and other metals in the Golconda region.
 The states of India which cover the parts of Deccan plateau are Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu. The state of Maharashtra covers a majority of the northern parts of the Deccan Plateau, and state of Chhattisgarh covers the northeast corner of the plateau. Andhra Pradesh state covers the east-central region of this Plateau, and the state of Karnataka covers the west central and a majority of the southern areas of the Deccan plateau, with the extreme south portion in the state of Tamil Nadu. The largest cities situated in the Deccan plateau are Karnataka and Bangalore. Some of the other major cities in the Deccan plateau are Hyderabad, the capital of the state of Andhra Pradesh, Aurangabad, Pune and Nagpur. Along the north and north-eastern edges of the hills of Deccan Plateau, the Bhil and Gond tribe live.
The states of India which cover the parts of Deccan plateau are Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu. The state of Maharashtra covers a majority of the northern parts of the Deccan Plateau, and state of Chhattisgarh covers the northeast corner of the plateau. Andhra Pradesh state covers the east-central region of this Plateau, and the state of Karnataka covers the west central and a majority of the southern areas of the Deccan plateau, with the extreme south portion in the state of Tamil Nadu. The largest cities situated in the Deccan plateau are Karnataka and Bangalore. Some of the other major cities in the Deccan plateau are Hyderabad, the capital of the state of Andhra Pradesh, Aurangabad, Pune and Nagpur. Along the north and north-eastern edges of the hills of Deccan Plateau, the Bhil and Gond tribe live.
Deccan plateau is also one of the major tourist attraction and some of the major attractions of this region include Aurangabad. It is known for its internationally-acclaimed Ajanta caves and Ellora caves. Another major attraction is the Bibi-ka-Maqbara or the mausoleum of the wife of Aurangzeb and the caves of Aurangabad. Badami was the former capital of the Chalukyas. It is presently a small rural town in the state of Karnataka. This place is famous for its attractive cave temples, engraved into the cliff face of a red sandstone hill.
Another major place of attraction is the Bijapur city. The magnificent and the largest dome in India and the worlds` second largest one, known as the Gol Gumbaz, present in this city. Other historical monuments include the Ibrahim Roza, an attractive tomb constructed by Adil Shah II in memory of his queen and the remains of Gagan Mahal are something which is a must to be seen site of this place.
Some of the other major attractions of the Deccan plateau include Ooty. It is located in the middle of Blue Mountains of the Nilgiris in the state of Tamil Nadu. This is one of the townships of the erstwhile British Empire in India and a renowned hill station. The Sunset Point and Watchtower provide a bird`s eye view of the distant hills and the flat countryside. Kozhikode (Calicut) is situated in the state of Kerala, was known as a commercial trading city during ancient times. Vasco-da-Gama landed in Kappad, a place situated in close proximity to Calicut in the year 1498. The city is renowned as the center of timber industry and for boat building. Gulbarga is placed in the Karnataka state of India. This little town is well-known for its links with the Bahamani kingdom of medieval India. Lists of monuments dating from 13th to the 15th century are present here. The Gulbarga fort is one of the major tourist attractions of this region.
The reliable history of the Deccan Plateau only starts with the 13th century A.D. In the earlier history, the major facts demonstrated are the emergence and growth of the Maurya Empire and details of the invasion of the Scythic tribes known as the Pallavas, Sakas and Yavanas. Finally, the region witnessed the institution of the power of the Kshaharata satraps in western parts of India.















