 Indian Puranic Villages are the origin point of the Indian social structure, its rules, regulations, norms, and lifestyle. These villages were small units of clustered households, living within the realm of spirituality and simplicity. There were several villages in India during the Puranic age and they were classified according to the prevailing kingdoms. These villages followed the administration of the ruling kings during that time.
Indian Puranic Villages are the origin point of the Indian social structure, its rules, regulations, norms, and lifestyle. These villages were small units of clustered households, living within the realm of spirituality and simplicity. There were several villages in India during the Puranic age and they were classified according to the prevailing kingdoms. These villages followed the administration of the ruling kings during that time.
Occupation in Indian Puranic Villages
The primary occupation during the Puranic age was the priesthood, thus every household had certain divine prejudices. These beliefs were followed down across the generations to be instilled in the present society. The Indian Puranic villages reflected unity and solemn social practices. The traditional festivals and principles came down from these villages. Several statues, temples, and monuments of the Indian Puranic villages are still revered and worshipped in various parts of the nation.
Puranic Villages in India
Several Indian Puranic villages have been excavated to develop them into heritage spots and historic sites. Some of the Puranic Villages in India are mentioned below:
Sarnath: The Sarnath and its surrounding areas make some of the prominent villages of Puranic India. It is situated 10 kilometers north-east of Varanasi City near the confluence of Yamuna and Ganga rivers in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. There is a popular deer park in Sarnath, where Gautama Buddha was known to first teach "Dharma". This is where the existence of Buddhist Sangha prevailed through enlightenment of the Kondana.
Dwarka: The Dwarka is an ancient city known for its religious influence across the country. It is the municipality of the Devbhoomi Dwarka district the Indian state of Gujarat. It is situated on the Okhamandal Peninsula towards the western shore on the right bank of the Gomti River. It is also one the "Chardhams" of Hindu pilgrims. It is often recognized as the ancient kingdom of Lord Krishna and believed to be the first capital of Gujarat.
Vrindavan: The Vrindavan is another holy Hindu and historical place at the Mathura district of the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. Vaishnavism considers it to be one of their most sacred places. It is situated in the region of Braj Bhoomi. As per Hinduism, Lord Krishna is known to spend most of his childhood here.
Bhitora village: The Bhitora was site of the sage Bhrigu. It was an important source of learning and the Bajpai family from Mauzmabad has played an important role in the development of this village. Famous for their grandeur and literary frame of mind, the people inhabiting Indian Puranic villages played a vital role in the formation of Indian society from its tender age.
Kanakhala: Kanakhala is the name of a village as mentioned in the Linga Purana. In this village the great sacrifice or Yajna of the Daksha took place. Gangadwara and Haridwar together make the Kanakhala village.
Kuntala: Kuntala Village is a village and Mandal located at Telengana in Andhra Pradesh. It is situated between the Nirmal Bhainsa highways towards kallur junction. It is mostly known for its waterfalls.
Harappa: The Harappa is an archaeological site presently located in Pakistan towards 24 kilometers west of Sahiwal. It is one of the most known Indian puranic village.
Jhansi: The Jhansi is a historic place located in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It lies in the Bundelkhand region on the banks of Pahuj River. It was anciently ruled by the Gurjar rajas.
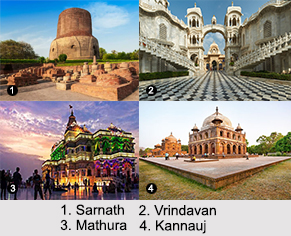 Kannauj: The Kannauj is another ancient city which is said to have been constructed by the Kanyakubja Brahmins of Shandilya. It also constitutes among three prominent families originally from Kannauj. It is served as the central of imperial dynasties during classical India. Earlier it was under the government of Maukhari dynasty and the later under Emperor Harsha of the Vardhana Dynasty. At present, it is known as the perfume capital of India.
Kannauj: The Kannauj is another ancient city which is said to have been constructed by the Kanyakubja Brahmins of Shandilya. It also constitutes among three prominent families originally from Kannauj. It is served as the central of imperial dynasties during classical India. Earlier it was under the government of Maukhari dynasty and the later under Emperor Harsha of the Vardhana Dynasty. At present, it is known as the perfume capital of India.
Nashik: It is an ancient city located in the northern region of the Indian state of Maharashtra on the banks of Godavari River. It is popularly known to be one of the Hindu pilgrimage sites where Kumbh Mela is held every twelve years.
Pushkar: It is an ancient city situated in the Ajmer district of the Indian state of Rajasthan. It is also one of the pilgrimage sites for both Sikhs and Hindus. Pushkar is known to have several temples around. Most of the ghats and temples are from the 18th century and later.






