Introduction
 Damodar River is located in the Indian states of Jharkhand and West Bengal. The Damodar River is considered to be one of the most important rivers in eastern India. Mineral resources in the Damodar Valley have made it a large-scale mining and industrial center. The river is also known as the "Sorrow of Bengal" because of its devastating floods in the plains of West Bengal. The river is famous all over the world for the Damodar Valley Corporation (DVC).
Damodar River is located in the Indian states of Jharkhand and West Bengal. The Damodar River is considered to be one of the most important rivers in eastern India. Mineral resources in the Damodar Valley have made it a large-scale mining and industrial center. The river is also known as the "Sorrow of Bengal" because of its devastating floods in the plains of West Bengal. The river is famous all over the world for the Damodar Valley Corporation (DVC).
Etymology of Damodar River
The name of the river has been derived from a Sanskrit word; "Dama" means rope and "udara" means belly. Thus, the meaning of the word Damodar is "rope around the belly". Damodar is another name of Lord Krishna. This name was given to Him when his foster mother tied him to a large urn. The river is also known as "Damuda" in a number of local dialects of Jharkhand. The word "Damu" means holy, whereas "da" stands for water. Thus, the meaning of the word Damuda is "holy water".
Geology of Damodar River
 Concentrations of heavy metals tend to increase, as the size of the sediments gets finer. However at two sites of Damodar River, near mining areas, the coarser particles show similar or even higher heavy metal concentrations than the finer ones. The superior residence time and presence of coarser particles from mining wastes are often responsible for higher metal content in the coarser size fractions. The chemical fractionation study shows that lithogenic is the major chemical phase for heavy metals.
Concentrations of heavy metals tend to increase, as the size of the sediments gets finer. However at two sites of Damodar River, near mining areas, the coarser particles show similar or even higher heavy metal concentrations than the finer ones. The superior residence time and presence of coarser particles from mining wastes are often responsible for higher metal content in the coarser size fractions. The chemical fractionation study shows that lithogenic is the major chemical phase for heavy metals.
The distribution of Si, Al, Fe, Mn, Cu, Zn, Ni and Cr in different grain-size fractions and geochemical association of Fe, Mn, Cu and Zn with <63-?m size fraction of bed sediments of Damodar River has been studied. Fe and Mn are the chief elements of the lithogenic lattice, made up of 34-63% and 22-59%, respectively, of total concentrations. Fe-Mn oxide and organic bound fractions are noteworthy phases in the non-lithogenic fraction in the bed of Damodar River.
Origin of Damodar River
 Damodar River begins near Chandwa village, Palamau district, on the Chota Nagpur Plateau in the Jharkhand state in eastern India. The river flows in the direction of east for about 592 km across the states of Jharkhand and West Bengal to the estuary of the River Hooghly. It has a number of tributaries and sub tributaries, such as Barakar, Konar, Bokaro, Jamnai, Haharo, Guaia, Ghari, Khadia and Bhera.
Damodar River begins near Chandwa village, Palamau district, on the Chota Nagpur Plateau in the Jharkhand state in eastern India. The river flows in the direction of east for about 592 km across the states of Jharkhand and West Bengal to the estuary of the River Hooghly. It has a number of tributaries and sub tributaries, such as Barakar, Konar, Bokaro, Jamnai, Haharo, Guaia, Ghari, Khadia and Bhera.
In some of the local languages of Jharkhand, the river is known is called Damuda. The term damu means sacred and da means water. The Damodar used to flow previously through Bengal on a direct west to east course and join the River Hooghly near Kalna. However, the river has changed its course and in its lower reaches most of the water flows into the Mundeswari River, which again merges with other rivers and finally most of the Damodar water debouches into the Rupnarayan River. The remaining water flows through the Damodar into the Hooghly south of Kolkata.
The Barakar is the most important tributary of the Damodar. It originates near Padma in Hazaribagh district and flows through Jharkhand before meeting the Damodar near Dishergarh in West Bengal. The Damodar and the Barakar divides the Chota Nagpur plateau. The rivers pass through hilly areas with great force, sweeping away whatever comes in their path. The Barakar, the great stone bridge build in 1913 and the successive iron bridge in 1946 interrupted two bridges on the Grand Trunk Road near Barhi in Hazaribagh district down.
Course of Damodar River
Damodar River has a length of about 592 km (368 mi.). The average rate of discharge of the river is about 10,500 cu ft/s. Chota Nagpur Plateau in Jharkhand is recognized as the origin of Damodar River. Damodar River flows through important cities like Asansol, Bokaro and Durgapur in West Bengal and Jharkhand. Earlier, Damodar River flowed through West Bengal, following a straight west to east route to join the River Hooghly near Kalna. Presently, the river follows an easterly route to journey through Jharkhand and West Bengal to the estuary of the Hooghly River for a length of near about 592 km. In its lower plains, the water of the river is emptied into the Mundeshwari River, which merges with other streams. The maximum volume of the river water enters the Rupnarayan River . The rest of the water flows south of Kolkata into the Hooghly River.
Tributaries of Damodar River
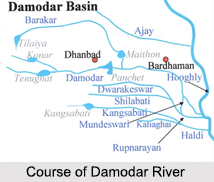 The tributaries and sub-tributaries of Damodar River are Barakar, Konar, Bokaro, Haharo, Jamunia, Ghari, Guaia, Khadia and Bhera. Out of this set of tributaries, the Barakar is considered to be the biggest tributary of Damodar. It has its source near Padma in Hazaribagh district and runs through Jharkhand. The Chota Nagpur Plateau is divided into three parts by the Barakar and the Damodar. The rivers flow through mountainous regions with enormous might, overwhelming anything that comes in their way. The Barakar destroyed two bridges close to Barhi on the Grand Trunk Road in Hazaribagh district and they are the huge rock bridge in 1913 and the succeeding iron bridge in 1946.
The tributaries and sub-tributaries of Damodar River are Barakar, Konar, Bokaro, Haharo, Jamunia, Ghari, Guaia, Khadia and Bhera. Out of this set of tributaries, the Barakar is considered to be the biggest tributary of Damodar. It has its source near Padma in Hazaribagh district and runs through Jharkhand. The Chota Nagpur Plateau is divided into three parts by the Barakar and the Damodar. The rivers flow through mountainous regions with enormous might, overwhelming anything that comes in their way. The Barakar destroyed two bridges close to Barhi on the Grand Trunk Road in Hazaribagh district and they are the huge rock bridge in 1913 and the succeeding iron bridge in 1946.
Floods Caused by Damodar River
Previously, Damodar River had been called as the "Sorrow of Bengal". Number of floods has adversely affected the lives of the residents living in the lower Damodar basin in the past. Some of the terrible floods were caused by the Damodar in the following years- 1770, 1855, 1866, 1873-1874, 1875-1876, 1884-1885, 1891-1892, 1897, 1900, 1907, 1913, 1927, 1930, 1935 and 1943. In the years 1770, 1855, 1913 and 1943, most of the Bardhaman town was flooded by the river.
In 1789, Maharaja Kirti Chand of Burdwan signed a contract with the British East India Company. Accordingly, the Maharaja had to pay an extra sum for the purpose of building and maintaining river banks to control floods. In the years 1866 and 1873, the Bengal Embankment Act came into being, according to which the authority to construct and preserve the river banks was passed to the administration.
Damodar Valley
Damodar Valley is spread across Hazaribagh, Ramgarh, Koderma, Giridih, Dhanbad, Bokaro and Chatra districts in Jharkhand and Bardhaman and Hooghly districts in West Bengal. It partially covers Palamu, Ranchi, Lohardaga and Dumka districts in Jharkhand and Howrah, Bankura and Purulia districts in West Bengal. The valley occupies an area of about 24,235 square kilometres (9,357 sq mi). It is considered to be one of the most industrialized parts of India. This valley is rich in deposits of coal. Damodar Valley is considered to be the chief center of coking coal in India. The important coalfields in the Damodar Valley basin are Jharia, Raniganj, West Bokaro, East Bokaro, Ramgarh, South Karanpura and North Karanpura coalfields.
 Damodar Valley Project : Damodar Valley Corporation, also known as DVC, is a government organization which came into force on July 7, 1948, by an Act of the Constituent Assembly of India. In this project four multipurpose dams on Damodar River were constructed to form a series of reservoirs - Tilaiya Dam, Maithon Dam, Konar Dam and Panchet Dam. The project provides for flood control, hydro-electricity, coal-fired thermal power plants, irrigation of about 950,000 acres (385,000 hectares) chiefly in West Bengal, afforestation, fish breeding, recreation and the general development of agriculture and industry throughout the valley. It is considered to be the first multipurpose river valley project of independent India.
Damodar Valley Project : Damodar Valley Corporation, also known as DVC, is a government organization which came into force on July 7, 1948, by an Act of the Constituent Assembly of India. In this project four multipurpose dams on Damodar River were constructed to form a series of reservoirs - Tilaiya Dam, Maithon Dam, Konar Dam and Panchet Dam. The project provides for flood control, hydro-electricity, coal-fired thermal power plants, irrigation of about 950,000 acres (385,000 hectares) chiefly in West Bengal, afforestation, fish breeding, recreation and the general development of agriculture and industry throughout the valley. It is considered to be the first multipurpose river valley project of independent India.
Threats to Damodar River
Damodar River banks are known to be rich in mineral resources. Thus, it could be exploited by industrialists. As a result, a number of coal-oriented industries came up in the Damodar basin. Most of them are coal washeries and glass, zinc, cement, thermal power, iron and steel and Government-owned coke oven plants. Thus, contamination of Damodar River commenced due to excessive and defective excavation, outmoded processing activities, oil, fly ash, poisonous metals and coal dust.



















