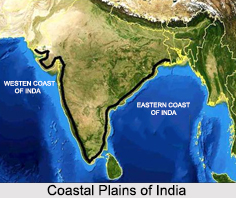
 Coastal Plains of India refer to the low flat areas which are situated adjacent to a water body, usually the sea. Coastal Plains are characterised by raised beaches and wave-cut platforms above the high water mark. It signifies that these Coastal Plains of India are basically the emerged floors of the seas adjacent to the land. The Great Indian Peninsular Plateau is fringed with narrow Coastal Plains. After the emergence of these lowlands, fluctuations in sea level, though limited to small areas, have brought about some changes in the general surface features of the littoral. The Deccan plateau has a coastal strip in the east and west. Coastal plains are generally separated from the interior land and have less vegetation in comparison. The Coastal Plains of India are rather extensive regions that significantly contribute to the physiographic aspect of the region.
Coastal Plains of India refer to the low flat areas which are situated adjacent to a water body, usually the sea. Coastal Plains are characterised by raised beaches and wave-cut platforms above the high water mark. It signifies that these Coastal Plains of India are basically the emerged floors of the seas adjacent to the land. The Great Indian Peninsular Plateau is fringed with narrow Coastal Plains. After the emergence of these lowlands, fluctuations in sea level, though limited to small areas, have brought about some changes in the general surface features of the littoral. The Deccan plateau has a coastal strip in the east and west. Coastal plains are generally separated from the interior land and have less vegetation in comparison. The Coastal Plains of India are rather extensive regions that significantly contribute to the physiographic aspect of the region.
Types of Coastal Plains of India
Coastal Plains of India are divided into two basic types and these are:
Eastern Coastal Plains runs from Tamil Nadu to West Bengal in the east.
Western Coastal Plains extends from Gujarat in the west to Maharashtra, Goa and Kerala.
Eastern Coastal Plain: The Eastern Coastal plain lies between West Bengal and Tamil Nadu. It stretches between the Bay of Bengal and the Eastern Ghats of India. 130 km is the average width of these plains. The region receives adequate rainfall between 40 to 120 inches, from Southwest and Northeast monsoons and has an average temperature above 30 degrees Celsius and high humidity. The Northern Circars, amidst Krishna River and Mahanadi River is the northern part. While the southern part, the Coromandel Coast, runs between Kaveri River and Krishna River. These plains have 6 regions; Andhra Plains, Kanyakumari Coast, Mahanadi Delta, Sandy Coastal regions, Krishna-Godavari deltas and Coromandel Coast.
 Western Coastal Plain: The Western Coastal plain lies between Kerala and Gujarat and stretches from the Arabian Sea to the Western Ghats. 50 km is the average width of these plains, much less than its eastern counterpart. These plains feature plentiful rivers and backwaters which result in forming estuaries. The Gulf of Kutch and the Gulf of Khambat lie on the northern part. The Western Coastal Plain is separated into three major parts the Malabar Coast, the Konkan Coast and the Gujarat Coast.
Western Coastal Plain: The Western Coastal plain lies between Kerala and Gujarat and stretches from the Arabian Sea to the Western Ghats. 50 km is the average width of these plains, much less than its eastern counterpart. These plains feature plentiful rivers and backwaters which result in forming estuaries. The Gulf of Kutch and the Gulf of Khambat lie on the northern part. The Western Coastal Plain is separated into three major parts the Malabar Coast, the Konkan Coast and the Gujarat Coast.
Other Coastal Plains of India
Off-shore bars have enclosed lagoons which run parallel to the coast in southern part of Kerala. These lagoons, also known as "Kayals", receive water of a large number of rivers before discharging that to the sea with which they are connected by narrow openings.
Further, there are several estuaries, the main ones being those of the Narmada River and Tapti River in Gujarat. It is blessed with cavernous natural harbours like Mumbai and Marmagao. Towards the south, the coastal plains of India are combined with salt water lakes that are called Lagoons. There are also sand bars or spits in their mouths. The coast is celebrated for its tranquil backwaters. The Rann of Kutch, the peninsulas of Kutch and Kathiawar and the Gujarat Plain stand out as major physiographic regions.















