 Ayurveda defines raktamokshana as the therapeutic withdrawal of blood from the body. It is the fifth major procedure that is used in Panchakarma therapy. However, raktamokshana is the most limited of the five major procedures. But this therapeutic procedure provides a rapid and sometimes dramatic reduction of symptoms in certain acute disorders especially where time is a critical factor. Comparatively, the other procedures of Panchakarma are much more comprehensive in their scope. The other procedures are also applied after raktamokshana is completed in order to provide deep cleansing of aama from the tissues and thereby remove the actual disease process.
Ayurveda defines raktamokshana as the therapeutic withdrawal of blood from the body. It is the fifth major procedure that is used in Panchakarma therapy. However, raktamokshana is the most limited of the five major procedures. But this therapeutic procedure provides a rapid and sometimes dramatic reduction of symptoms in certain acute disorders especially where time is a critical factor. Comparatively, the other procedures of Panchakarma are much more comprehensive in their scope. The other procedures are also applied after raktamokshana is completed in order to provide deep cleansing of aama from the tissues and thereby remove the actual disease process.
Rakta dhatu and pitta dosha are very closely connected and at the same time their function is interrelated. Rakta or the blood is also called `Jeevan` or life. Rakta dhatu is represented by blood, which is formed and regulated by the liver, bone marrow and spleen. It performs the pitta associated work. That is why, toxins appear due to excess pitta and they get concentrated in the blood. If there is any disturbance in the circulation or constitution of blood then it causes diseases. When excessive pitta related aama exists in the blood, it gets transported to the body`s periphery, where it often produces characteristic symptoms like skin hypersensitivity and skin inflammation. Once the aama is removed, rakta metabolism improves and the blood can perform its function very effectively. When the toxins associated with the pitta dhatu are removed from the body, the functioning of pitta regains balance. So, raktamokshana is the therapy that is used in order to reduce the impurities of the blood. Good blood sustains life and helps maintain the physiological equilibrium that is necessary for sound health.
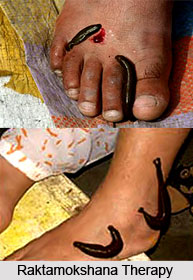
In simple terms, raktamokshana means extracting blood from the body through certain specific equipments like Shrugna (horn of an animal) and Alabu (a substance prepared from dried bottle gourd). Raktamokshana efficiently treats blood related diseases that include the skin disorders, eczema, rashes and chronic itching. This therapy is also used in treating enlarged liver or spleen, headaches, hypertension and gout. All these diseases that are caused due to impurities in blood can be successfully treated with this therapy. Raktamokshana is often prescribed towards the end of summer and during the autumn season. In these seasons, the pitta tends to become aggravated due to the dominance of agni bhuta in the environment. However, this treatment is contraindicated for infants, pregnant women, aged people and even those who are suffering with anaemia, bleeding problems, cirrhosis of the liver and leukaemia.
Administration of Raktamokshana
The process of raktamokshana is carried out very carefully. Snehana and swedana do not have to precede raktamokshana. It is on the day of the treatment, the patient simply lies on a table and a small amount is withdrawn intravenously. The blood is examined for smell, colour, consistency, clotting and viscosity characteristics. The particular features of the blood will indicate the quality of function in the pitta zone. The venipuncture is sealed by medicated gauze and a pressure bandage is applied for a short time. After about one hour, the patient can get up.
Thus, Ayurveda proves that raktamokshana helps in purifying blood and make it free from any waste products or toxins.




















