 Son River of central India is one of the largest southern tributaries of the Ganges after Yamuna River. Rising in Madhya Pradesh and with a length of 784 kilometres (487 miles), the Son River is one of the largest rivers in India. The river is an extension of the Narmada valley and the Kaimur range is an extension of the Vindhya Range in the lower levels. The Son River is a wide and shallow river and forms pools of water in the remaining parts of the river. The floodplain of the river is narrow and is only, 3 to 5 kilometers wide. The river used to change its course frequently in the past, which has been checked to some extent with the dam at Dehri and also with the construction of Indrapuri Barrage. Dehri is the major town situated on the Son River.
Son River of central India is one of the largest southern tributaries of the Ganges after Yamuna River. Rising in Madhya Pradesh and with a length of 784 kilometres (487 miles), the Son River is one of the largest rivers in India. The river is an extension of the Narmada valley and the Kaimur range is an extension of the Vindhya Range in the lower levels. The Son River is a wide and shallow river and forms pools of water in the remaining parts of the river. The floodplain of the river is narrow and is only, 3 to 5 kilometers wide. The river used to change its course frequently in the past, which has been checked to some extent with the dam at Dehri and also with the construction of Indrapuri Barrage. Dehri is the major town situated on the Son River.
Geography of Son River
The Son valley is geologically almost a continuation of that of the Narmada River to the southwest. It is largely forested and sparsely populated. The valley is bordered by the Kaimur Range to the north and the Chota Nagpur plateau to the south.
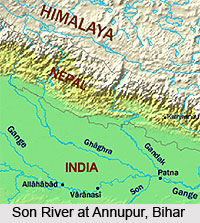 Course of Son River
Course of Son River
The Son River originates in the Amarkantak in Madhya Pradesh, in the east direction of the origin of Narmada River. It then flows in the north-northwest direction through Madhya Pradesh before turning in the east direction where it meets the Kaimur range. The river starts flowing in the parallel direction of the Kaimur range in the east-northeast direction through Uttar Pradesh and Bihar and joins the Ganga River just above Patna, the capital of Bihar.
Tributaries of Son River
The main tributaries of the Son River are Rihand River and the Koel River. The other tributaries are Gopad River and Kanhar River.
Dams and Bridges on Son River
The first dam on the Son River, Old Anicut Dam was built in 1876 A.D. by the British government which was an example of modern technology. The dam is abandoned and presently hosts a remarkable place to visit and view marvellous evenings during sun set. The Indrapuri Barrage is one of the longest dams in India that was constructed in 1968. It is located nearly 9 km from Dehri. The Ban Sagar Dam in Madhya Pradesh is a multipurpose river Valley Project on the Son River.
The 1440-metre Abdul Bari Bridge near Arrah was completed in 1862. The modern Son Bridge built in Deolond, Shahdol district of Madhya Pradesh was inaugurated in 1986.
Nearby Attractions from Son River
Amarkantak is a unique natural heritage which is very rich in biodiversity. Apart from this, it is source of origin of three important rivers. The Kabra Khurd is a beautiful place on the banks of the Son River, primarily due to its picnic spots. Some other places of interest here are the Rohtasgarh Fort, Aina Mahal, Jami Masjid and Habsh Khan`s crypt, Ganesh Temple, The Hanging House, Rohtasan Temple and Devi Temple, Diwan-e-khas and Diwan-e-aam. There are many waterfalls in this area that falls from the top of Kaimur hill towards east and joins the Son River.















