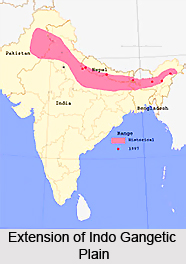
 The Indo Gangetic plain is a large fertile alluvial region of India stretching from the Indus River system in Pakistan to the Punjab Plain (in both Pakistan and Haryana) and the Haryana Plain to the delta of the Ganga in Bangladesh where it is called Padma.
The plain is homogenous with some common features of river erosion and changes in river channels. It is surrounded by the lofty Himalayas on the north, by the Vindhya and Satpura range and the Chota Nagpur Plateau on the south and the Iranian Plateau. The name of the region comes from Indus and the Ganges, the twin rivers flowing in the region. While according to some geographers, the Indo -Gangetic Plains are divided into several parts the Indus Valley, the Punjab Plain, the Haryana Plains, and the middle and lower Ganga some say that the western parts consists of the Punjab Plain and the Harayana Plain the eastern part consists of the Ganga Brahmaputra drainage systems.
The Indo Gangetic plain is a large fertile alluvial region of India stretching from the Indus River system in Pakistan to the Punjab Plain (in both Pakistan and Haryana) and the Haryana Plain to the delta of the Ganga in Bangladesh where it is called Padma.
The plain is homogenous with some common features of river erosion and changes in river channels. It is surrounded by the lofty Himalayas on the north, by the Vindhya and Satpura range and the Chota Nagpur Plateau on the south and the Iranian Plateau. The name of the region comes from Indus and the Ganges, the twin rivers flowing in the region. While according to some geographers, the Indo -Gangetic Plains are divided into several parts the Indus Valley, the Punjab Plain, the Haryana Plains, and the middle and lower Ganga some say that the western parts consists of the Punjab Plain and the Harayana Plain the eastern part consists of the Ganga Brahmaputra drainage systems.
The Terai region constitutes the northern boundary of the Indo Gangetic plains. The Great Indian Desert in Rajasthan forms the southern boundary of the plains. It continues in the east along the base of the hills of Central Highlands to the Bay of Bengal. The northern part of the Central Highlands consists of Aravalli Range of eastern Rajasthan and the southern part of the Central Highlands consists of the Aravalli Plateau, which merges with the Vindhya ranges.
The rivers traversing the region are the Beas, the Chambal, the Chenab, the Gomti, the Indus, the Ravi, the Sutlej and the Yamuna, because of these rivers the soil here is rich in silt. This makes it one of the most fertile regions in the world suitable for agriculture. The crops cultivated here are rice, wheat, maize, sugarcane and cotton. The southwest monsoon is the main source of rainfall along with the rivers, which provide water for major irrigation works.
This region is also historically very significant because it is here that several Indian kingdoms had their territory. They were the Gupta Empire, Kanauj Empire, Magadha Empire the Maurya Empire, the Mughal Empire and the Sultanate of Delhi. At present the cities part of this region are Ahmedabad, Delhi, Dhaka, Faisalabad, Hyderabad (Pakistan), Kanpur, Karachi, Kolkata, Lahore, Lucknow, Ludhiana, Multan, Patna, Rawalpindi-Islamabad, and Surat



















