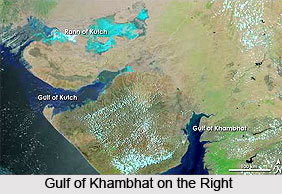
 The Gulf of Khambhat is an inlet of the Arabian Sea along the west coast of India, in the state of Gujarat. Earlier, it was known as the Gulf of Cambay. The Narmada and the Tapti rivers evacuate into the Gulf. Stretching for about 80 miles, the Gulf of Khambhat therefore ideally splits the Kathiawar peninsula. The Gulf is not very deep and has abundant shoals and sandbanks. The high tide of the Gulf varies in terms of height and races with great speed. During the low tide, the bottom is completely dry for some distance below the town of Khambhat.
The Gulf of Khambhat is an inlet of the Arabian Sea along the west coast of India, in the state of Gujarat. Earlier, it was known as the Gulf of Cambay. The Narmada and the Tapti rivers evacuate into the Gulf. Stretching for about 80 miles, the Gulf of Khambhat therefore ideally splits the Kathiawar peninsula. The Gulf is not very deep and has abundant shoals and sandbanks. The high tide of the Gulf varies in terms of height and races with great speed. During the low tide, the bottom is completely dry for some distance below the town of Khambhat.
Geography of Gulf of Khambhat
The periphery of the Gulf of Khambhat is an extensive area of estuarine habitats. The Narmada, Tapti, Mahi and Sabarmati rivers drain into it. These rivers have deposited alluvium over large areas as the marine recession has united Saurashtra with mainland of Gujarat. There are extensive areas of intertidal mud and sand flats in the deltas of the Mahi and Sabarmati rivers. There are some coral reefs around small inlets in the western part of the Gulf.
Climate of Gulf of Khambhat
The inlet experiences dry tropical monsoon climate with an average annual rainfall of about 800 mm. The monsoon begins on June or July and ends in September. The rainfall is erratic in occurrence, duration, and intensity. The winters are generally cool and dry.
Flora and Fauna of Gulf of Khambhat
The area is home to mangrove forest and Avicennia marina. Earlier, species of Rhizophoraceae were also available but now have disappeared completely from most of the sites. The area is the shelter of 62 species of water birds. The coastal marshes and mudflats provide feeding areas for large numbers of herons, egrets, storks, and ibises which breed in groves of trees in nearby towns and villages.
Significance of Gulf of Khambhat
Since ancient times, the gulf has been an important commercial center. The ports join central India to the maritime trading activities of the Indian Ocean. The significant seaports on the Gulf are Bharuch, Surat, Khambhat, Bhavnagar and Daman. Khambhat was an important port in the middle ages but after the silting of the harbour, Surat rose to prominence as the most important harbour of the Mughal Empire.















