Introduction
 Godavari River is considered to be one of 7 sacred Indian rivers. It is India`s second longest river. Godavari River also has the distinction of being the largest river in the Indian peninsula considering its length, catchment area and discharge. It has been serving as a life giver and sanctifier for most of the towns in Andhra Pradesh and Maharashtra. Pushkar Mela, a major bathing festival is held on the banks of the river, after every 12 years. One of the ships of the Indian Navy called INS Godavari has derived its name from the name of the river.
Godavari River is considered to be one of 7 sacred Indian rivers. It is India`s second longest river. Godavari River also has the distinction of being the largest river in the Indian peninsula considering its length, catchment area and discharge. It has been serving as a life giver and sanctifier for most of the towns in Andhra Pradesh and Maharashtra. Pushkar Mela, a major bathing festival is held on the banks of the river, after every 12 years. One of the ships of the Indian Navy called INS Godavari has derived its name from the name of the river.
Geography of Godavari River
Godavari River runs for a length of about 1,465 kilometers. It covers 8 Indian states of Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, Puducherry (Yanam), Odisha and Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh and possesses about 313,000 square kilometers of drainage area.
Geology of Godavari River
 River Godavari is under the serious threat as a result of the growing civilization and industrialization. The river has been drying at a disturbing rate due to the pollution fashioned by the factories. The main reason behind the pollution of Godavari River is the small Nakavaggu rivulet that joins the Manjira, a tributary of the Godavari. Nakavaggu rivulet is not a source of life in its course. The rivulet is bounded by the extremely productive agricultural land, which is polluted by a huge number of industries located near the twin cities of Secunderabad and Hyderabad. However the 72 industries in the Patancheru Industrial area dumps the chemicals and waste into the water and thus changes the geology of the soil vastly. Some of the major diseases such as lung cancer, leukemia, and liver cancer in the region are due to this water pollution. The government of India has been constantly taking steps to save the river water from further pollution.
River Godavari is under the serious threat as a result of the growing civilization and industrialization. The river has been drying at a disturbing rate due to the pollution fashioned by the factories. The main reason behind the pollution of Godavari River is the small Nakavaggu rivulet that joins the Manjira, a tributary of the Godavari. Nakavaggu rivulet is not a source of life in its course. The rivulet is bounded by the extremely productive agricultural land, which is polluted by a huge number of industries located near the twin cities of Secunderabad and Hyderabad. However the 72 industries in the Patancheru Industrial area dumps the chemicals and waste into the water and thus changes the geology of the soil vastly. Some of the major diseases such as lung cancer, leukemia, and liver cancer in the region are due to this water pollution. The government of India has been constantly taking steps to save the river water from further pollution.
The Godavari River, the third largest river in India and has been sampled for particulate inorganic and organic carbon (PIC, POC), particulate nitrogen (PN), and particulate amino acids (PAA, including 2 hexosamines (HA)). During the dry season, the river is abundance of particulate organic matter (POM) in the upper reaches and is relatively fresh and autochthonous. However, in the lower reaches it is tarnished and inorganic suspended matter content is much higher here.
In the wet season heavy rains cause a basin-wide flushing of humus from entire catchment area. As a consequence, POM in the river is mainly corrupted and allochthonous. Yearly transport of the Godavari River rises to around 2.81× 10sup6/sup ton POC, 0.29× 10sup6/sup ton PN and 0.10× 10sup6/sup ton particulate amino acid nitrogen. These amounts categorize the Godavari River to one of the most significant organic carbon transporting rivers in the world.
Godavari River Basin
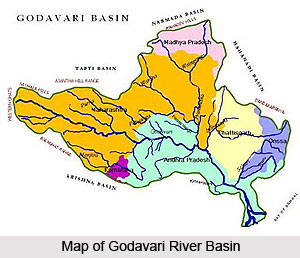 The Godavari River has ample tributaries and distributaries that flow in the Godavari River Basin. Some of the main rivers flowing in the Godavari river basin are as follows -
The Godavari River has ample tributaries and distributaries that flow in the Godavari River Basin. Some of the main rivers flowing in the Godavari river basin are as follows -
After the Ganges and the Indus Rivers the Godavari River is a sacrosanct river in India. It originates in the Western Ghats near Trimbak in Nashik district of Maharashtra. It then flows in the east across the Deccan Plateau traversing through the states of Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh. It flows in a southeastern direction in order to evacuate in the Bay of Bengal through two mouths. The major tributaries of the Godavari are Indravati River, Manjira River, Bindusara River and Sabari River. It travels a distance of 1,465 km. before draining into the Bay of Bengal.
The Kolab River is the tributary of River Godavari and flows in the Koraput districts. The Kolab originates from the Sinkaran hills of the Eastern Ghats in Koraput districts. The river covers a catchment area of 20400 sq. kms. The Gupteswar Temple is an important pilgrimage along the river. The Indravati River is a tributary of the Godavari River, located in central India. The river rises in the Eastern Ghats in Orissa and flows westwards to join the Godavari, thus forming the boundary between Maharashtra and Chhatisgarh states at some places. Most of the River Course of Indravati is through dense forests of Bastar. The famous `Chitrakoot` falls forms on Indravati River, some 40 km from Jagdalpur in Chhatisgarh.
The Bandiya River is a tributary of Godavari, flowing in Gadchiroli district of Maharashtra. Pranhita River flows on the edge of Gadchiroli district in Maharashtra and Adilabad district in Andhra Pradesh. The name Pranhita is derived from the nature of combined flow of the rivers Painganga and Wainganga. The Wainganga river originates about 12 Km from Mundara village of Seoni district in the southern slopes of the Satpura Range of Madhya Pradesh, and flows south through Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra in a very meandering course of roughly 360 miles.
Sati River is one of tributaries of Godavari River and flows in the district of Gadhchirli. Khbragadi River is one of tributaries of Godavari River. Chulband River is one of tributaries of Godavari river. Other than the Kanhan River, the Pench, Jam, Kulbehra, Shakkar and Doodh rivers also flow in the region of Sausar in Madhya Pradesh. Kanhan river flows in the Southern direction through the western parts of Chhindwara Tahsil and converges with the Wenganga river.
Nag River is a tributary of Godavari River. The Pench River is a tributary of Godavari river and flows in the border areas of Chhindwara and Seoni Districts in Maharashtra. Kolhar River is one of tributaries of River Godavari, flowing in Nagpur. The Sur River is a tributary of Godavari River and flows in the districts of Bhandara and Nagpur in Maharashtra. Bawanthadi River starts it journey from the Kurai plateau of Seoni District in Madhya Pradesh. Eventually, the river enters Bhandara District of Maharashtra by flowing towards south and functions as an interstate boundary between two states all along its middle course.
The Wagh River is also known as the Daman Ganga River in Goa.
 The Wardha River is the distributary of Godavari and a significant tributary of Pranhita River. The Penganga River is also known as the Painganga River and is considered as the chief river of the Yavatmal district in the Maharashtra state in India. Geographically Vidarbha lies on the northern part of Deccan Plateau and the Vidarbha River lies in this hilly terrain. Arunavati River is one of the chief tributaries of Penganga River. The river flows across Darwha and certain areas of Kelapur.
The Wardha River is the distributary of Godavari and a significant tributary of Pranhita River. The Penganga River is also known as the Painganga River and is considered as the chief river of the Yavatmal district in the Maharashtra state in India. Geographically Vidarbha lies on the northern part of Deccan Plateau and the Vidarbha River lies in this hilly terrain. Arunavati River is one of the chief tributaries of Penganga River. The river flows across Darwha and certain areas of Kelapur.
A principal tributary of the Painganga River, the Adan river flows in the state of Maharashtra. The Adan River originates in the Washim district of Maharashtra (India) and flows across a curve, north, east and south, and finally converges with the Painganga River. The river Kayadhu on entering the district from the northwest turns at a right angle flows northeastwards under the influence of a similar turn of the spur and joins the Penganga. The Vena River play a vital role in agriculture of Nagpur. The crops grown in the territory have a strong bearing on this river.
Bor River is one of the tributaries of Godavari River in India. Yashoda River is one of the tributaries of Godavari River in India. Dham River is one of the tributaries of Godavari River in India. Bhakalee River is one of the tributaries of Godavari River in India. Ramganga River is the most important factor for the maintenance of Jim Corbett Park. In fact without this river, there would be no Corbett Park established. This river is the tributary of Godavari and the largest of the precious few persistent sources of water in the Park.
The start of the Bombala River is in the Brown Mountain area with other rivers emptying into it. Charghad River, Maad River, Manjra River, Manhaad River, Lendi River and Terna River are some of the tributaries of Godavari River flowing in India. The Tavarja River is a tributary of Godavari and flows through the Latur district of Maharashtra. The Kelna River flows in the administrative district of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Bindusara River is one of the tributaries of Godavari River in India.
The Karanja river is a distributary of Godavari River with mythological importance. The location of Karanja River co ordinates latitude 18degree 4` 60 N and longitude 77degree 4` 60 E. Karanja river basin covers around 2422 square kilometers. Devani River is one of the tributaries of Godavari River in India. The Kadakpurna River flows through the district of Parbhani, which was previously known as Prabhavatinagar. This river plays a significant role in the lifestyle of the people residing in this region. The Dudhna River flows in the district of Parbhani, which lies in the east central part of Maharashtra. The river flows parallel to the Hyderabad railway line that is about 16 km south of the Dudhna River.
The Kapra River flows in the hydrographic soil, through the state of Maharashtra. This tributary of Godavari river coordinates from the latitude 19degree 22` 60 N to longitude 76degree 54` 0 E. Kham River is one of the tributaries of Godavari River in India. Shivna River is an important tributary of Godavari, flowing in the state of Rajasthan. In old maps this river is written as SAU and SEU. Pravara River is an important river in the western parts of Maharashtra. It is one of the main tributaries of the Godavari River. The Mula river is an important river in India that originates at the Mulshi Dam in Taluka Mulshi in Pune district in the Western Ghats province of the Indian state Maharashtra.
Kadwa river is one the most important tributaries of Godavari River. The Nandur Madhmeshwar Dam lies at the convergence point of Godavari and Kadwa Rivers. The Darna River rises from the highlands of the Sahyadris; it is one of the major tributaries of Godavari. The Darna River flows through an area of hydrographic soil.
Course of Godavari River
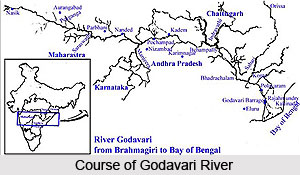 The Godavari River is one of the major waterways in central India; it originates in the Western Ghats and flows eastwardly across the Deccan Plateau between the states of Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh, then crossing Andhra Pradesh it turns to flow in a southeast direction until it finally flows into the Bay of Bengal through two mouths. Its tributaries are Indravati River, Bindusara River, Moosi River, Manjira River and Sabari River.
The Godavari River is one of the major waterways in central India; it originates in the Western Ghats and flows eastwardly across the Deccan Plateau between the states of Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh, then crossing Andhra Pradesh it turns to flow in a southeast direction until it finally flows into the Bay of Bengal through two mouths. Its tributaries are Indravati River, Bindusara River, Moosi River, Manjira River and Sabari River.
The river arises only 80 kilometres from the Arabian Sea and it flows 1,465 km to get emptied into the Bay of Bengal. Just above Rajahmundry or the Rajahmahendravaram, there is a dam for the supply of water for irrigation. Below Rajahmundry, the river splits into two streams that broaden into a large river delta that is extensive navigable irrigation-canal system. The Dowleswaram Barrage or Dhawaleshwaram links the region to the Krishna River delta in the southwest.
The Indrawati, the Wardha, the Pench, the Wainganga, the Kanhan and Penganga rivers discharge an enormous volume of water in the Godavari system. The Godavari River has a total drainage area of almost 313,000 km² that includes more that one state. The Manjra River is its major tributary.
Origin of Godavari River
 The Godavari River rises near the Trimbak in the district of Nasik in the Indian state of Maharashtra. The river runs almost for a length of 1,465 km and has a total catchment area of 31mha. The river flows in the eastward direction through the states of Maharashtra and joins the Bay of Bengal in Andhra Pradesh. The main tributaries of the River Godavari are Penganga, Pranahita, Indravati, Manjeera, Sabari and Manair. It is the second largest river in India.
The Godavari River rises near the Trimbak in the district of Nasik in the Indian state of Maharashtra. The river runs almost for a length of 1,465 km and has a total catchment area of 31mha. The river flows in the eastward direction through the states of Maharashtra and joins the Bay of Bengal in Andhra Pradesh. The main tributaries of the River Godavari are Penganga, Pranahita, Indravati, Manjeera, Sabari and Manair. It is the second largest river in India.
Trimbakeshwar, origin of Godavari
Godavari"s source is in Trimbakeshwar, Maharashtra. Trimbakeshwar temple is a famous pilgrim spot in India. It is actually the temple of Lord Shiva, in the village Trimbak. Trimbak lies in the shadow of the Brahmagiri Hill, the actual source of the holy Godavari river. Trimbakeshwar is one of the 12 jyotirlingas and the eighth one in the series of Lord Shiva. Particularly this one is considered to be the main Jyotirlinga. Monday is a sacred day here and Shivratri is the holy day of Shiva Puja of the year, which is celebrated here with pomp and show. The Goddess in this temple is called Trimbakeshwari. Raju Balaji Baji Rao who ruled Maharashtra constructed this temple. Later, many Maratha kings contributed in several ways to improve the condition of the temple. Very close to the temple, Papaharini Theertham is situated. People take holy bath here before visiting the temple. This place is created by river Godavari after descending from Brahmagiri.
Features of Trimbakeshwar Temple
The temple is situated in a hilly region called Sahyagiri. It is exactly located between three hills namely, Brahmagiri, Nilagiri and Kalagiri. Brahmagiri is best known as the most sacred place of river Godavari or the Brahma Sthalam. The Sun, Moon and Agni form three eyes and are located at diverse directions on this Jyotirlinga. Inside the main linga, there are three more lingas noticeable. There are the three deities- Brahma, Vishnu and Maheshwara. There is a belief that, anybody who performs puja for this Jyotirlinga is considered as actually worshipping all these three Gods together. There are images of various deities inside, namely the Gangadevi, Jaleswara, Rameswara, Gautameswara, Kedarnatha, Rama, Krishna, Parasurama and Lakshmi Narayana. The temple also has several monasteries and samadhis of saints.
The extraordinary feature of the Jyotirlinga in Trimbak is its three faces, embodying Lord Brahma, Lord Vishnu and Lord Rudra. The linga has started to erode due to the excessive use of water. The Lingas are covered by a crown full of jewels. The crown is placed over the Gold Mask of the Tridev (Brahma-Vishnu-Mahesh). The crown is said to exist there from the age of Pandavas. It is displayed to the tourists every Monday from 4-5 pm. The entire black stone temple is known for its architecture and sculpture.
 Legends related to Godavari River
Legends related to Godavari River
Brahmadev worshipped Lord Trivikram when he came to Satya Loka (earth) with the holy water of the Ganges, to get the river Ganges held up by Lord Shankar on his head, to flow. There was a famine of 24 years and people were dying of hunger. Varun - the God of Rains, pleased with Gautama arranged rains every day in Gautama`s ashram in Trimbakeshwar. Gautama sowed rice in the surrounding fields of his Ashram in the morning, and with it fed a large group of rishis, who took shelter in his Ashram on account of the famine. The blessings of the rishis increased the merit of Gautama. Lord Indra`s position became shaky because of this. Thus Indra brought the clouds to rain all over Trimbakeshwar, so that the famine would be over and the rishis would go back. Although the famine was over, Gautama urged the Rishis to stay back and kept on feeding them. Once he saw a cow grazing in the fields. He drove her away by throwing Darbha grass. The weak cow died by this. It was Jaya - Parvati`s friend, who had taken the form of a cow. This news upset the Rishis and they refused to stay at his Ashram. Gautama requested Rishis to show a way out of this sin. He was advised to go to Lord Shiva and request him to release the Ganges. They told him that a bath in the Ganges would free him of his sins. Gautama then practiced penance on the peak of Brahmagiri for 1000 years. Lord Shiva was pleased by his worships and gave him the Ganges.
However, Ganges was not prepared to part with Lord Shiva. He made the Tandav Nritya on the peak of Brahmagiri. Frightened by this action, Ganges appeared on Brahmagiri. Later on, Ganges appeared in the Trimbak Tirtha. The Ganges then appeared in Gangadwar, Varaha-tirtha, Rama-Laxman tirtha, Ganga Sagar tirtha. However, still, Gautama could not bathe in her waters. Then, Gautama surrounded the river with grass and made a vow to her. The flow stopped there and the tirtha came to be called Kushavarta. It is from this Kushavarta that the river Godavari flows up to the sea. Kushavarta is now known as Kushavartham.
Pilgrimages at the origin of Godavari River
After descending further, the river comes across many better-known places, located very close to its origin place. Gangadwar or Gangadwaram are the places where the river flows beneath the branches of trees in a narrow place. Very close to Paapa Haarini Theertham, Mahadeva and Ganga Matha temples are located. On the way to Brahmagiri, Vithal Mandir and Ganga Dwar are visible. Caves of 108 Shiva Lingas are one of the most visited places where Maharshi Gautama worshipped lord Shiva. Parashuram temple and Ambika alayam are some more places which can be visited.
The origin of Godavari River or the Trimbakeshwar temple can be reached by road from Nashik by covering only 35 KM. Nasik is well connected by train also. The journey from Nashik to Trimbakeshwar is across the forest. People can stay here for one whole day and have to reach back Nashik for staying. The nearest airport is Oghur, which is 16 Kms from Nashik. The nearest railway station is Nasik.
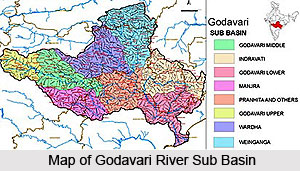
Tributaries of Godavari River
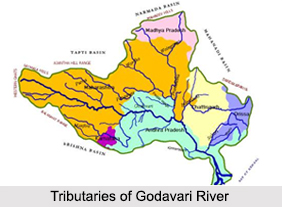 Tributaries of River Godavari can be classified as the left bank tributaries which include the Purna, Pranhita, Indravati and Sabari River and the right bank tributaries Pravara, Manjira and Manair River. The left bank coverings nearly 59.7 percent of the total catchment area of the basin and the right bank tributaries contribute 16.1 percent of the basin. The Tributaries of River Godavari are responsible for the supply of water in the states of Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh.
Tributaries of River Godavari can be classified as the left bank tributaries which include the Purna, Pranhita, Indravati and Sabari River and the right bank tributaries Pravara, Manjira and Manair River. The left bank coverings nearly 59.7 percent of the total catchment area of the basin and the right bank tributaries contribute 16.1 percent of the basin. The Tributaries of River Godavari are responsible for the supply of water in the states of Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh.
Some of the Tributaries of River Godavari are the following:
Pravara River: Pravara River is the smallest tributary of Godavari River. It is the only tributary of Godavari which originates in the Western Ghats in Maharashtra. The Bhandardara Dam is constructed across this river forming the Arthur Lake.
Indravati River: The Indravati River is a tributary of the Godavari River, located in central India. The river rises in the Eastern Ghats in Odisha and flows westwards to join the Godavari, thus forming the boundary between Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh states at some places. Most of the river course of Indravati is through dense forests of Bastar.
Pranhita River: Pranhita River flows on the edge of Gadchiroli district in Maharashtra and Adilabad district in Andhra Pradesh. The name Pranhita is derived from the nature of combined flow of the rivers Penganga and Wainganga. The river then flows up to Sironcha. The river finally empties into the Godavari River, near Sironcha in Maharashtra.
href="https://www.indianetzone.com/purna_river_indian_river" class="clsCrossLink" title="Purna River">Purna River: Purna River is a major left-bank tributary of Godavari River originating in the Ajanta Range of hills in Aurangabad District, Maharashtra. It is a prime river in the Marathwada region of Maharashtra running for about 373 km before it confluences with Godavari River south of Purna city in the Parbhani district.
Wainganga River: The Wainganga River originates from Mundara village of Seoni district in the southern slopes of the Satpura Range of Madhya Pradesh, and flows through Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra in a very meandering course of roughly 360 miles.
Manjira River: Manjira River is a tributary of Godavari River and a significant river in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. Nizam Sagar Dam was constructed across the Manjira River between Achampet and Banjapalle villages of the Nizamabad district in Andhra Pradesh.
Kinnerasani River: The Kinnerasani River is one of the important tributaries of Godavari. The scenic beauty of the course along Kinnerasani River is eye catching and panoramic. The Kinnerasani Dam provides water at Palvoncha for power generation and also for irrigation facilities to the nearby farmers through lift irrigation.
Sabari River: The Sabari River is one of the significant tributaries of Godavari, flowing in Chhattisgarh. It originates from the western slopes of Eastern Ghats in Odisha from Sinkaram hill ranges. It is also known as Kolab River in Odisha.
Religious Significance of Godavari River
 The Godavari is a river that runs from western to southern ends of India and forms one of the largest river basins in India. With a length of 1465 km, it is the second longest river in India, second to The Ganges, and the longest in southern India. It originates near Trimbak in Nashik District of Maharashtra state and flows east across the Deccan Plateau into the Bay of Bengal near Yanam and Antarvedi in East Godavari district of Andhra Pradesh.
The Godavari is a river that runs from western to southern ends of India and forms one of the largest river basins in India. With a length of 1465 km, it is the second longest river in India, second to The Ganges, and the longest in southern India. It originates near Trimbak in Nashik District of Maharashtra state and flows east across the Deccan Plateau into the Bay of Bengal near Yanam and Antarvedi in East Godavari district of Andhra Pradesh.
In India, a river does not merely serve the purpose of irrigating the fields. They are also considered to be of extreme religious significance. Infact, they are worshipped as Goddesses and numerous festivals and rituals are celebrated on the banks of these revered rivers. Apart from Ganga and Yamuna, Godavari also holds the exceptional religious importance in India. Godavari is one of the sacred rivers in India. According to the Puranas, River Ganga should only be visited after the visit to the Godavari. There are several pilgrimage places on the banks of the river Godavari. The major spot of pilgrimage is Trimbakeshwar, the ancient temple of Lord Shiva. Nanded Takht Sri Hazur Sahib is one of the sacred places among the Sikhs, while Bhadrachalam is the temple of Lord Rama and many more.
Godavari is sometimes referred to as the `Ganga of the South`. After every twelve years, a major bathing festival held is called as Pushkaram held on the banks of the Godavari River. Scores of people take a holy dip in the sacred waters of Godavari to cleanse themselves of all their sins. Some of the well-known personalities who took bath in its holy water include Baladeva 5000 years ago and the saint Chaitanya Mahaprabhu 500 years ago.
Legends associated with Godavari River
As per mythology, Godavari, one of the most sacred rivers of India, is believed to be the sister of Ganga. It is believed to have originated from the "jata" of Lord Shiva, while he was meditating on Mount Kailash.
 A legend has it that the Sage Gautama lived in the Brahmagiri Hills at Trimbakeshwar with his wife Ahalya. The Rishi kept his stock of rice in a granary. Once, a cow entered his granary and ate up the rice. When the Rishi tried to ward the cow away with Durbha grass, it fell dead. The cow is considered as an extremely holy animal in Hinduism. The Rishi wished to atone for the sin of "Gohatya" - killing a sacred cow. He prayed to Lord Shiva and requested him to divert the river Ganges to purify his hermitage. Lord Shiva was pleased with the Rishi so appeared in his Trimbaka manifestation and diverted the river Ganges to flow past his homestead. Satisfied with the devotion of Sage Gautama, Lord Shiva also gave some water from his Kamandalu. When the waters of the just descended Godavari River flowed over the dead cow, Sage Gautama sprinkled the water Lord Shiva had given him and the dead cow came back to life. Thus, Sage Gautama was redeemed of all his sins. Ganga was brought down to Trimbakeshwar by Sage Gautama, she is known here as Gautami. It is also known as Godavari, since the river helped Gautama to relieve him off "Gohatya".
A legend has it that the Sage Gautama lived in the Brahmagiri Hills at Trimbakeshwar with his wife Ahalya. The Rishi kept his stock of rice in a granary. Once, a cow entered his granary and ate up the rice. When the Rishi tried to ward the cow away with Durbha grass, it fell dead. The cow is considered as an extremely holy animal in Hinduism. The Rishi wished to atone for the sin of "Gohatya" - killing a sacred cow. He prayed to Lord Shiva and requested him to divert the river Ganges to purify his hermitage. Lord Shiva was pleased with the Rishi so appeared in his Trimbaka manifestation and diverted the river Ganges to flow past his homestead. Satisfied with the devotion of Sage Gautama, Lord Shiva also gave some water from his Kamandalu. When the waters of the just descended Godavari River flowed over the dead cow, Sage Gautama sprinkled the water Lord Shiva had given him and the dead cow came back to life. Thus, Sage Gautama was redeemed of all his sins. Ganga was brought down to Trimbakeshwar by Sage Gautama, she is known here as Gautami. It is also known as Godavari, since the river helped Gautama to relieve him off "Gohatya".
It is also believed that a childless woman conceives a child when she drinks the holy waters of the River Godavari.
As per another legend, at Panchavati, located in Nashik on the banks of the River Godavari, Lakshman (brother of Rama) had cut off the nose of Surpanakha (Sister of Ravana). Both Rama and Lakshmana are believed to have taken the ritualistic bath in Godavari, upon hearing about the demise of their father, King Dasharatha.
Another legend has it that Sage Gautama was married to the very beautiful Ahalya. Lord Indra upon learning about her beauty had lusted for her. To get closer to her, Lord Indra disguised himself as Sage Gautama and embraced her. Upon seeing this, the angry sage cursed Ahalya to turn into stone and also cursed Lord Indra to a life full of diseases. The curse to Ahalya was later absolved by Lord Rama. After severe and extreme penance, the curse to Lord Indra was absolved when he took a dip in the holy waters of Godavari. The River Godavari was brought down upon the earth to end the curse of Lord Indra.
Pilgrimages near Godavari River
The banks of Godavari River consist of several pilgrimage sites. They are as listed below.
•Trimbakeshwar - One of the 12 Jyotirlingas and ancient temple of Lord Shiva.
•Nashik - One of the four Sinhastha Kumbh Mela.
•Paithan - Saint Eknath"s native place, Jayakwadi dam and Sant Dnyaneshwar Udyan.
•Nanded - Takht Sri Hazur Sahib; one of the five most sacred places for Sikhs.
•Basar - Sri Gyana Saraswati Temple.
•Dharmapuri - Lord Narasimha Swami Temple.
•Kaleshwaram - Sri Kaleswara Mukhteswara Swamy Temple at Triveni Sangamam.
•Bhadrachalam - Lord Rama Temple.
•Rajahmundry - Center for Telugu Literature.
•Pattiseema - A village where a Hindu temple is on a small hill on an island in Godavari.
•Antarvedi - Laxmi Narasimha Swami temple.
•Konaseema - Scenic delta of Godavari.
Ecological Significance of Godavari River
 India supports about 10% of the world`s Biological Diversity, with just 2% of the worlds land area, thus making it the seventh richest bio-diversity country in the world. This difference bestows a great responsibility on the government with the responsibility to protect and conserve the rich floral, faunal & ecological diversity of Godavari river basin. The protection is well carried out by constructing a network of sanctuaries and national parks, which cover areas of ecological and biological importance. The State of Andhra Pradesh is located strategically and its geographical variation is thought to be as one of the rich bio-diversity states in India.
India supports about 10% of the world`s Biological Diversity, with just 2% of the worlds land area, thus making it the seventh richest bio-diversity country in the world. This difference bestows a great responsibility on the government with the responsibility to protect and conserve the rich floral, faunal & ecological diversity of Godavari river basin. The protection is well carried out by constructing a network of sanctuaries and national parks, which cover areas of ecological and biological importance. The State of Andhra Pradesh is located strategically and its geographical variation is thought to be as one of the rich bio-diversity states in India.
In the terms of ecological significance, a survey declared Andhra Pradesh to be the fifth largest state in India adhering to the factor of ecological importance. Moreover, this state has the longest coastline that stretches over 1000 Kms. The state has two mighty river systems of Krishna and Godavari. The state has wide and different vegetation types enriched by a diversity of flora and fauna. Andhra Pradesh is located strategically in the central region of the Indian sub-continent and thus has representatives of the magnificent Indian plant and animal life. Its varied countryside ranges from the hills of Eastern Ghats and Nallamallas to the shoreline of Bay of Bengal and thus supports speckled ecotypes, which again supports a rich diversity of flora and fauna. The forest in the state can largely be divided into four major biotic provinces.
The ecological effect of the Godavari River in various regions is as follows
Deccan Plateau - 53 %
Eastern Highland - 11 %
Central Plateau - 35 %
East Coastal Plains - 1 %
 The vegetation found in the state is largely made of dry deciduous style with a mixture of precious trees like Teak, Dalbergias, Pterocarpus, Terminalias, Anogeissus and so on. The hills of Eastern Ghats add highly to the biological diversity and provide centers of endemism for plants, birds and lower forms of animal life. The varied environment harbors a assortment of fauna, including tiger, panther, sambar, wolf, cheetal, wild dog, chowsingha, black buck, hyena, sloth bear, nilgai, gaur, chinkara and a number of birds and reptiles. The long sea coast offers the inhabiting place for sea turtles, the back water of Pulicat lake are the feeding and breeding grounds for flamingo and grey pelican, the estuaries of river Godavari and Krishna initiates the growth of rich mangrove forests with fishing cat and otters as key stone species.
The vegetation found in the state is largely made of dry deciduous style with a mixture of precious trees like Teak, Dalbergias, Pterocarpus, Terminalias, Anogeissus and so on. The hills of Eastern Ghats add highly to the biological diversity and provide centers of endemism for plants, birds and lower forms of animal life. The varied environment harbors a assortment of fauna, including tiger, panther, sambar, wolf, cheetal, wild dog, chowsingha, black buck, hyena, sloth bear, nilgai, gaur, chinkara and a number of birds and reptiles. The long sea coast offers the inhabiting place for sea turtles, the back water of Pulicat lake are the feeding and breeding grounds for flamingo and grey pelican, the estuaries of river Godavari and Krishna initiates the growth of rich mangrove forests with fishing cat and otters as key stone species.
The Godavari river basin also possesses of some exceptional and endemic plants like Cycas beddomei, Terminalia pallida, Syzygium alternifolium, Pterocarpus santalinus, Shorea talura, Psilotum nudam, Shorea tumburgia and so on. Similarly the double banded or the jerdon`s courser, the slender loris, the golden gecko are rare and dying out inhabiting the basin.
Andhra Pradesh has a total network of 22 Sanctuaries and 4 National Parks encompassing an area of 12,579.205 Sq. Kms. or 4.57 % of the geographical area of the entire basin. The states lying in this basin are rich in forests and diverse flora and fauna thus providing ample capacity for promoting eco-tourism. The natural beauty of the state has not been exposed to the visitors till now. The government has taken up the plan to open up the Protected Area Network of the State for all the visitors. Each of the Wildlife Sanctuary and National Park of the state has its own significance and has something unique for the visitors.
Developments at the Site of Godavari River
Godavari River splits into 2 streams which widen into a large river delta providing an extensive navigable canal irrigation system, below Rajahmundry in Andhra Pradesh. The irrigation canals are a part of Dowleswaram Barrage. They link the delta of Godavari River with the River Krishna Delta in the southwest, making the region one of the richest rice-growing areas in India. Sriram Sagar Dam on Godavari River serves the purpose of irrigation. In Nizamabad district in Andhra Pradesh, there is a multipurpose project on the sacred river called the Sriramsagar Project. Some of the other developments on Godavari River are Gangapur Dam, Ghatghar Dam and Jayakwadi Dam.
Places of Interest along Godavari River
Godavari River has several major districts, cities of India, towns and villages along it. In Maharashtra, Nanded district, the cities of Trimbak, Paithan and Nashik, town of Kopargaon and village of Mahegaon Deshmukh are located along the Godavari River. In Andhra Pradesh, the city of Rajahmundry, the towns of Kovvur and Narsapuram and the village of Tallapudi lie on the banks of Godavari River. In Telangana, Mancherial, Kaleshwaram, Bhadrachalam, Basara, Godavarikhani and Dharmapuri are located along the Godavari River.
Threats to Godavari River
Godavari River is under serious threat as a result of the growing civilization and industries. The river has been drying at a disturbing rate due to the pollution fashioned by the factories. The main reason behind the pollution of Godavari River is the small Nakavaggu rivulet that joins the Manjira River. Nakavaggu rivulet is not a source of life in the course of the river. Domestic wastes have also caused pollution in the river basin.



















