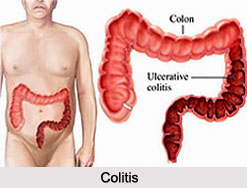
 Colitis is an Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) in which there is chronic inflammation of the inner lining of the colon. It mainly affects the tissue that lines the gastrointestinal system i.e., the large and small intestine.
Colitis is an Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) in which there is chronic inflammation of the inner lining of the colon. It mainly affects the tissue that lines the gastrointestinal system i.e., the large and small intestine.
Types of Colitis
Types of colitis include Ulcerative Colitis (UC), Lymphocytic Colitis, Diversion Colitis, Crohn"s Colitis, Chemical Colitis, Ischemic Colitis, Fulminant Colitis, Infectious Colitis, Collagenous Colitis, Microscopic Colitis and Atypical Colitis. A well-known subtype of infectious colitis is known as the Pseudomembranous Colitis, which results from infection by a toxigenic strain of Clostridium difficile, however parasitic infections can also cause colitis. Irritable bowel syndrome, a separate disease, has been called Spastic Colitis.
Causes of Colitis
The causes of colitis are also similar to that of Diarrhoea. The continuous intake of heavy, spicy food and the use of stale, polluted and adulterated substances cause problems in the digestive system and it decomposes after reaching the intestines. Thus, the intestine fills up with stool due to non-cleansing of bowels causing contamination as well. However, natural efforts are made for this polluted matter to come out of the body.
 Symptoms of Colitis
Symptoms of Colitis
Usually the signs and symptoms of colitis include pain, tenderness in the abdomen, depression, rapid weight loss, aches and pains within the joints, fatigue, changes in bowel habits in increased frequency, fever; swelling of the colon tissue, redness of the surface of the colon, ulcers on the colon in ulcerative colitis, which can bleed, mucus in the stool, blood in stool and rectal bleeding. Other symptoms of Colitis may include gas, bloating, indigestion, heartburn, reflux, Gastro oesophageal reflux disease, cramps, urgency and many other uncomfortable aches in the gastrointestinal system.
Diagnosis of Colitis
Common tests which reveal these signs of Colitis include X-rays of the colon, testing the stool for blood and pus, sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy. Additional tests include stool cultures and blood tests, including blood chemistry tests.
Treatment of Colitis
Treatment of Colitis through nature care is said to be the best. Magnetic Therapy and Hipbath is beneficial in this disease. A change in diet and can be effective in treating the symptoms of colitis and easing the side effects. These include reducing the intake of complex carbohydrates, lactose products, refined sugar, soft drinks, caffeine and spicy foods. Buttermilk is very useful for Colitis. The four naval correcting asanas may also be practised for the prevention of recurrent loose motions due to the displacement of naval towards lower side. Surgery of Colitis is required only when the patient suffers from regular or permanent flare-ups, especially in cases of Fulminant Colitis.