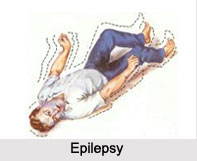
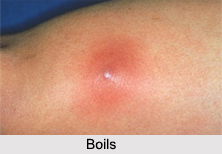
 Boils, also known as "Furuncles"; is a skin disease. Boils are deep Folliculitis which is primarily an infection in the hair follicles of a human. Boils are referred to as a painful sore with a hard core filled with pus and can form in any part of the body. Boils are caused by a type of bacterium known as "Staphylococcus Aureus", but may also be caused by other bacteria or fungi that are found on the surface of the skin. If boils occur repeatedly, it is called "Chronic Furunculosis". Boils can be transmitted from one person to another, as well.
Boils, also known as "Furuncles"; is a skin disease. Boils are deep Folliculitis which is primarily an infection in the hair follicles of a human. Boils are referred to as a painful sore with a hard core filled with pus and can form in any part of the body. Boils are caused by a type of bacterium known as "Staphylococcus Aureus", but may also be caused by other bacteria or fungi that are found on the surface of the skin. If boils occur repeatedly, it is called "Chronic Furunculosis". Boils can be transmitted from one person to another, as well.
Stages of Boils
Boils may begin as a tender, pinkish-red, swollen, firm area in the skin. Eventually, it feels like a water filled balloon or cyst. In the last stage, the centre of the area softens and becomes filled with infection-fighting white blood cells. The collection of white blood cells, bacteria, and proteins is called "Pus". Eventually, the pus forms a head that can be surgically opened or spontaneously drain out through the surface of the skin.
Causes of Boils
Boils are caused due to different reasons and the key reason is the infection of hair follicles that result in localised collection of pus and dead tissue. Generally people having immune system disorders, diabetes, poor hygiene or malnutrition is more susceptible to developing boils, than others. However, boils can occur in healthy, hygienic individuals, as well; mainly due to over scratching a particular area of the skin. Boils are frequently caused by Hidradenitis Suppurativa and sometimes, the anti-perspirant deodorants can cause boils in the armpits, as well. Bacteria present on the skin, like Staphylococci, also causes boils.
Symptoms of Boils
The symptoms related to boils are swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, fever and general ill feeling, when the infection is severe. Sometimes unpleasant smell may emit from boils, especially when it is drained or when emission of pus is on the way. The areas of a human body where boils occur most commonly are the back, stomach, underarms, shoulders, face, lip, eyes, nose, thighs and buttocks, etc. However, boils can be found elsewhere, as well.
Types of Boils
Several types of boils can develop in a human body. Every boil begins as a red mark and gradually grows in size. Though the basic shape of most of the boils is same, boils may have different types of formations. Sometimes, different causes are also found to be present in different types of boils. The different types of boils are mentioned below:
•Furuncle is one of the most common boils, caused by an infection of hair follicle by the bacterium Staphylococcus Aureus
•Carbuncles, which tend to grow in clusters; the Hidradenitis Supparativa, mostly caused when sweat glands inflame and become infected
•Cystic Acne, caused by a plug in the hair follicle
•Pilonidal Cysts, also known as rectal boils, are another type of boils, which are usually recurrent and can cause severe pain
Treatment of Boils
Boils can be treated through medicinal practices like Ayurveda, Homeopathy, Indian Naturopathy, etc. However, in India, most people treat boils through self-care. They apply a warm compress or soak the boil in warm water, which helps alleviating the pain and stimulates draining of the pus. The area is then washed with antibacterial soap and bandage properly, once the boil drains completely.
However, the treatment is different in case of serious boil infection or carbuncles. The patients are advised to apply Epsom salt paste to the affected area for preventing the growth of bacteria. This paste can also reduce boils by absorbing pus and drying up the lesion. Apart from the above mentioned methods, people treat boils through home remedies, using water treatments, or through aromatherapy, as well.
Prevention from Boils
People often use these preventive measures to minimise the risk of developing boils or bacterial skin infections. Cleansing skin properly with soap and water, and taking showers rather than tub baths; not sharing washcloths, towels, or facial cosmetics with others; cutting down on greasy or fatty foods and snacks; washing hands before touching the face; using antiseptic soaps and shower gels, etc. are some of the most effective preventive actions taken for boils. A doctor should be consulted if Furunculosis is a persistent problem.