 Caste system in India is a composite structure of different social classes in the Hindu religion. Caste system in India has a long history dating back to the ancient past. It dates back to that era when people used to believe that people were born into a particular social status. They also believed that experiences in past lives and good deeds can actually reincarnate one into higher social strata in the next life. The Indian caste system has gone places with the changes that have taken place in the society. Education has been massively instrumental in bringing a change in the state of mind though a large section of a society, mostly the older generation is still under the curse of this social ostracism.
Caste system in India is a composite structure of different social classes in the Hindu religion. Caste system in India has a long history dating back to the ancient past. It dates back to that era when people used to believe that people were born into a particular social status. They also believed that experiences in past lives and good deeds can actually reincarnate one into higher social strata in the next life. The Indian caste system has gone places with the changes that have taken place in the society. Education has been massively instrumental in bringing a change in the state of mind though a large section of a society, mostly the older generation is still under the curse of this social ostracism.
Development of Caste System in India
The development of the caste system in India never seems to be having any universally accepted history as such. Though there is a general speculative faith that the earliest settlers to this land, the Indo-Aryans might have actually established the caste system, gradually placing them in the higher ladder of the society. There is a whole lot of controversy regarding the theory of the Indo-Aryan migration. The Hindu scriptures can also be taken into consideration in this regard, which has some passages that can be interpreted to sanction the caste system. This also indicates that the caste system is not an essential part of the Hindu religion. The Vedas or the most ancient `shruti` texts emphasise very less on the caste system, same is maintained in a hymn from the Rig Veda. Later scriptures like Bhagavad Gita and Manu Smriti propounds four Varnas, to be God`s creation. There is a general idea believed by scholars that may be in the initial phases the caste system was a bit flexible. Migration from one caste to the other was possible by switching jobs. Various passages from Manu Smriti and other scriptures emphasise that the caste system in India was originally non-hereditary.
Varna and Jati in India
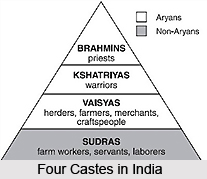
Ancient Hindu scriptures have the citations of four varnas or colour, which is the basic social class in the caste system in India. Bhagavad-Gita says that varnas are decided on the grounds of Guna which is the amalgamation of the five elements of ether, air, fire, water and earth, and Karma which is the concept of action. In accordance with the powers of the born nature, works of Brahmins, Kshatriya, Vaishya, and Sudras differ. Four varnas that are mentioned by other shastras are the Brahmins destined as teachers, scholars and priests, the Kshatriyas as kings and warriors, the Vaishyas were the trading class and the Shudras were agriculturists, service providers, and some artisan groups. These are further classified into jatis. Another group excluded from the main society was called Parjanya or Antyaja. This is the group of former untouchables who were considered either the lower section of Sudras or beyond the caste system altogether. Varna and jati are two different concepts.
 Indian Caste and Social Status
Indian Caste and Social Status
India is a multicultural, multilingual country which adopts a liberal attitude towards its diverse religious practices. One can find the prevalence of the caste system more in Hinduism than any other religion. Caste system in India has a history and it defines how caste has evolved through the ages. Caste and social status has always been quite puzzling. In the British era, they tried to equalize the caste system in India with the class system. Castes are the divisions, into which a certain section of the community belongs, which also enjoy social status accordingly. What is generally meant by the social status is the prestige or the honour that is being attached to one`s position in the society. An individual might acquire more power and privilege due to a characteristic; this puts him among the privileged group of the people who enjoy high status. Brahmins are the priestly class, the protector of religion while the Kshatriyas hold the political power. Therefore caste and social status were inter-related. A higher caste individual was always looked with awe and reverence.
British Impact over Caste System in India
Some scholars are of the view that the caste system in India was never so rigid until the British interfered in the caste related issues in India. They almost equated caste with the class system that exist in their country and in the process tampered with the long established caste system. Even among the Dalits there were the distinctions of high and low, and conflicts often took place. Caste system was seen as a pointer of social standing, intellectual ability and occupation. Hence the British wanted to include it in the census.
Caste system in India is a complex system of several distinctions, which have divided the society into the high and low strata. Lots of measures at present have been taken up by the government for the enhancement of backward castes who do not have a social standing.






































