 Azamgarh is a district of Uttar Pradesh. Azamgarh once formed a part of the ancient Kosala kingdom. Kosala figured prominently among the four powerful monarchies of northern India during the time of the Buddha. Azamgarh hardly possess any remains of much antiquarian value. In every tehsils of this district are some deserted sites, forts and tanks.
Azamgarh is a district of Uttar Pradesh. Azamgarh once formed a part of the ancient Kosala kingdom. Kosala figured prominently among the four powerful monarchies of northern India during the time of the Buddha. Azamgarh hardly possess any remains of much antiquarian value. In every tehsils of this district are some deserted sites, forts and tanks.
History of Azamgarh
In the ancient times, Azamgarh was inhabited by old indigenous people like Bhars, Soeris and Cherus who represented the descendants of the aborigines of this area. Relics of numerous embankments, tanks, caverns and stone forts are found in this district which still bears out their energy and skill.
In 18th century, Azamgarh was included in the sirkars of Jaunpur district and Ghazipur in the subah of Allahabd and was held by the Mohhabat Khan, popularly known as the Raja of Azamgarh. In his time the prosperity of Azamgarh was at its zenith. On September 18, 1832 Azamgarh district was formed. After the struggle of 1957-58 no major events except the Gaurakshini or the anti-cow slaughter movement of 1893 occurred in the district till the close of the 19th century.
Azamgarh was in the front line of the Quit India Movement. The very day the district Congress office at Azamgarh was seized; and several arrest were made, the principal one being the arrest of Sita Ram Ashthana.
Geography of Azamgarh
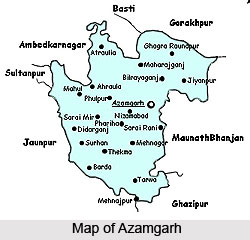
 Azamgarh district is located in Uttar Pradesh. The district occupies an area of 4234 sq.km. The district is bounded by Mau district on the east, Gorakhpur district on the north, Ghazipur on the south-east, Jaunpur on the south- west, Sultanpur district on the west and Ambedkar Nagar district on the north-west.
Azamgarh district is located in Uttar Pradesh. The district occupies an area of 4234 sq.km. The district is bounded by Mau district on the east, Gorakhpur district on the north, Ghazipur on the south-east, Jaunpur on the south- west, Sultanpur district on the west and Ambedkar Nagar district on the north-west.
The district of Azamgarh comprises a somewhat irregularly shaped tract of country lying south of the Ghaghra river. The other rivers flowing through the district are Tons River (Tamasa), Choti Saryu, and Tamsha. The lakes found in the district are Kotail, Jamuawan, Gumadih, Kumbh, Pukh, Asaune and the largest of all of them is the Gambhiran.
The climate of the district is moist and relaxing except in winter and hot seasons. The year may be divided into four seasons. The average annual rainfall in the district is 1021.3 mm. and it varies from 979.1 mm. at Deogaon to 1060.4 mm. at Azamgarh. On an average, in a year there are 50 rainy days.
Demography of Azamgarh
According to 2011 census, Azamgarh has a population of 46, 16,509. Males form 22, 89,336 of the population and females 23, 27,172. The average literacy rate of Azamgarh is 62.The largest part of the community belongs to the Hindu religion. Muslims constitutes 15% of the district population. There are minorities of other religions including Sikhism, Christianity, Buddhism, and Jainism.
Culture of Azamgarh
 Azamgarh is rich in cultural and religious activities as the district lies in the eastern part of Uttar Pradesh. The traditional languages of the district are Bhojpuri language and Purvi. The principal deities worshipped by the people are Lord Brahma, Lord Vishnu, Lord Shiva, Goddess Lakshmi, Lord Rama, Lord Hanuman, Lord Ganesha and nine forms of Goddess Durga. The practice of taking a holy dip in river is also famous.
Azamgarh is rich in cultural and religious activities as the district lies in the eastern part of Uttar Pradesh. The traditional languages of the district are Bhojpuri language and Purvi. The principal deities worshipped by the people are Lord Brahma, Lord Vishnu, Lord Shiva, Goddess Lakshmi, Lord Rama, Lord Hanuman, Lord Ganesha and nine forms of Goddess Durga. The practice of taking a holy dip in river is also famous.
The important festivals celebrated by the people of Nizamgarh are Nav Durga, Ramnavami, Krishna Janmasthmi, Shivratri, Diwali, Dussehra and Holi.
Majority of the Muslims in the district belong to the Sunni sect. They are mostly weavers. Sikh, Christians, Buddhists and Jains are found in very minor number in the district.
Education of Azamgarh
The government of Azamgarh is concerned in providing quality education to its citizens. There are primary schools, Higher Secondary Schools and Degree Colleges. There is also a medical college and a polytechnic centre. At present there are no engineering colleges at Azamgarh. The government is aiming at Total Literacy Campaign. Post Literacy Campaign has also been sanctioned.
Economy of Azamgarh
The main occupation of the people of Azamgarh is agriculture. They are involved in the cultivation of pulses, oil seeds, sugar cane, and potato. They also grow fruits like mango and guava. The major industries of the district are Kisan Sahkari Chini Mills Ltd., Benarasi Sari Udyog, in Mubarakpur, Black Pottery, in Nizamabad district, Foods and Allied Products, and Chemicals and Allied Products.
 Food products like biscuits, toffee and other confectionery articles are produced at Azamgarh. The raw materials used in this industry are sugar, maida, suji and ghee.
Food products like biscuits, toffee and other confectionery articles are produced at Azamgarh. The raw materials used in this industry are sugar, maida, suji and ghee.
Candles, Ayurvedic medicines, soap, perfumed oil and paints are also manufactured in Azamgarh. These units use wax, colour, castic soda etc. as raw material.
The major crops cultivated here are pulses, oil seeds, sugar cane, and potato.
Tourism of Azamgarh
Places of interest in Azamgarh includes the shrine of Bhiron Baba, Temple of Thakurji, Mubarakpur, Gurudwara, Ashram of Dattatreya Rishi, and Ashram of Durvasa Rishi.
People like to visit the district. Some important places in Azamgarh are Azamgarh City, Nizamabad, Maharajganj, Mubarakpur, Mehnagar, Durvasa, Dattatreya, Govindsahab and Avantikapuri (Awank).



















