 Cordia macleodii is considered as an important medicinal plant of India. It is widely distributed in the moist and dry deciduous forests up to 1200 metres in peninsular India, mostly from Chota Nagpur to Tamil Nadu. The major common names of this medicinal plant are Dahipalas, Dhagan, Dhaiman, Dhen-Gan in Hindi; Bilichalle, Doddachalle, Hadang, Hirichalle in Kannada; Bhoti, Dahipalas, Daiwas, Dhaiwan in Marathi; Baurlo, Bhoto, Bohurolo in Oriya; Palandekku in Tamil; and Botuku, Peddabattuva, Peddabotuku in Telugu.
Cordia macleodii is considered as an important medicinal plant of India. It is widely distributed in the moist and dry deciduous forests up to 1200 metres in peninsular India, mostly from Chota Nagpur to Tamil Nadu. The major common names of this medicinal plant are Dahipalas, Dhagan, Dhaiman, Dhen-Gan in Hindi; Bilichalle, Doddachalle, Hadang, Hirichalle in Kannada; Bhoti, Dahipalas, Daiwas, Dhaiwan in Marathi; Baurlo, Bhoto, Bohurolo in Oriya; Palandekku in Tamil; and Botuku, Peddabattuva, Peddabotuku in Telugu.
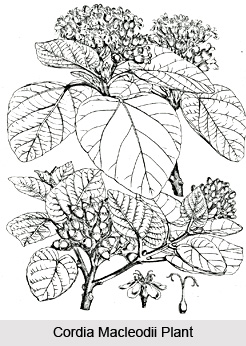
Morphology of Cordia macleodii
Cordia macleodii plant is a medium-sized, evergreen tree. Generally these plants are 12 metres tall with smooth whitish or grayish barks. Leaves are alternate and generally, 5-20 centimetres long. The flowers of these medicinal plants are white in colour and are polygamous. Fruits of these plants are generally known as drupes. The size of fruits varies from 1.3 centimetres to 2 centimetres. These are long, ovoid, acute and inedible.
Medicinal Uses of Cordia macleodii
This plant is useful for its medicinal properties. In several communities the bark is used for the treatment of jaundice. The plant extract also possesses wound healing, hepato-protective and aphrodisiac properties. The leaves of the plant are also known to have radical scavenging activity.
This article is a stub. You can enrich by adding more information to it. Send your Write Up to content@indianetzone.com



















